The V proteins of paramyxoviruses bind the IFN-inducible RNA helicase, mda-5, and inhibit its activation of the IFN-beta promoter
- PMID: 15563593
- PMCID: PMC535396
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407639101
The V proteins of paramyxoviruses bind the IFN-inducible RNA helicase, mda-5, and inhibit its activation of the IFN-beta promoter
Abstract
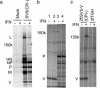
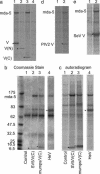
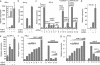
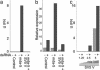
Most paramyxoviruses circumvent the IFN response by blocking IFN signaling and limiting the production of IFN by virus-infected cells. Here we report that the highly conserved cysteine-rich C-terminal domain of the V proteins of a wide variety of paramyxoviruses binds melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (mda-5) product. mda-5 is an IFN-inducible host cell DExD/H box helicase that contains a caspase recruitment domain at its N terminus. Overexpression of mda-5 stimulated the basal activity of the IFN-beta promoter in reporter gene assays and significantly enhanced the activation of the IFN-beta promoter by intracellular dsRNA. Both these activities were repressed by coexpression of the V proteins of simian virus 5, human parainfluenza virus 2, mumps virus, Sendai virus, and Hendra virus. Similar results to the reporter assays were obtained by measuring IFN production. Inhibition of mda-5 by RNA interference or by dominant interfering forms of mda-5 significantly inhibited the activation of the IFN-beta promoter by dsRNA. It thus appears that mda-5 plays a central role in an intracellular signal transduction pathway that can lead to the activation of the IFN-beta promoter, and that the V proteins of paramyxoviruses interact with mda-5 to block its activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bovine parainfluenza virus type 3 accessory proteins that suppress beta interferon production.Microbes Infect. 2007 Jul;9(8):954-62. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2007.03.014. Epub 2007 Apr 7. Microbes Infect. 2007. PMID: 17548221
-
LGP2 plays a critical role in sensitizing mda-5 to activation by double-stranded RNA.PLoS One. 2013 May 9;8(5):e64202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064202. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23671710 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the beta interferon promoter by unnatural Sendai virus infection requires RIG-I and is inhibited by viral C proteins.J Virol. 2007 Nov;81(22):12227-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01300-07. Epub 2007 Sep 5. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17804509 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of type I interferon production by paramyxoviruses.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Sep;29(9):539-47. doi: 10.1089/jir.2009.0071. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19702509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Jan;31(1):27-31. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0057. Epub 2010 Oct 15. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 20950133 Review.
Cited by
-
Complete genome sequence analysis of an American isolate of Grapevine virus E.Virus Genes. 2013 Jun;46(3):563-6. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0872-0. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Virus Genes. 2013. PMID: 23296875
-
Innate immune responses to duck Tembusu virus infection.Vet Res. 2020 Jul 8;51(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00814-9. Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32641107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1 (ADAR1) suppresses the induction of interferon by measles virus.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(7):3787-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06307-11. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22278222 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of type 1 diabetes genes on disease progression: similarities and differences between countries.Curr Diab Rep. 2012 Oct;12(5):447-55. doi: 10.1007/s11892-012-0310-7. Curr Diab Rep. 2012. PMID: 22895852 Review.
-
Viral evasion of intracellular DNA and RNA sensing.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Jun;14(6):360-73. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.45. Epub 2016 May 13. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27174148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lamb, R. A. & Kolakofsky, D. (2001) in Fields' Virology, eds. Fields, B. N., Knipe, D. M., Howley, P. M. & Griffin, D. E. (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia), Vol. 1, pp. 1305–1340.
-
- Wang, L.-F. & Eaton, B. (2001) Infect. Dis. Rev. 3, 52–69.
-
- Goodbourn, S., Didcock, L. & Randall, R. E. (2000) J. Gen. Virol. 81, 2341–2364. - PubMed
-
- Sen, G. C. (2001) Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 255–281. - PubMed
-
- Grandvaux, N., tenOever, B. R., Servant, M. J. & Hiscott, J. (2002) Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 15, 259–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

