Striatin assembles a membrane signaling complex necessary for rapid, nongenomic activation of endothelial NO synthase by estrogen receptor alpha
- PMID: 15569929
- PMCID: PMC534607
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407492101
Striatin assembles a membrane signaling complex necessary for rapid, nongenomic activation of endothelial NO synthase by estrogen receptor alpha
Abstract
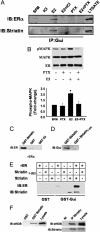
Steroid hormone receptors (SHRs) are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate gene expression. SHRs also mediate rapid, nongenomic cellular activation by steroids. In vascular endothelial cells, the SHR for estrogen, estrogen receptor (ER) alpha, is _targeted by unknown mechanisms to a functional signaling module in membrane caveolae that enables estrogen to rapidly activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-Akt kinase pathways, and endothelial NO synthase (eNOS). Here we identify the 110-kDa caveolin-binding protein striatin as the molecular anchor that localizes ERalpha to the membrane and organizes the ERalpha-eNOS membrane signaling complex. Striatin directly binds to amino acids 183-253 of ERalpha, _targets ERalpha to the cell membrane, and serves as a scaffold for the formation of an ERalpha-Galphai complex. Disruption of complex formation between ERalpha and striatin blocks estrogen-induced rapid activation mitogen-activated protein kinase, Akt kinase, and eNOS, but has no effect on ER-dependent regulation of an estrogen response element-driven reporter plasmid. These findings identify striatin as a molecular scaffold required for rapid, nongenomic estrogen-mediated activation of downstream signaling pathways. Furthermore, by demonstrating independent regulation of nongenomic vs. genomic ER-dependent signaling, these findings provide conceptual support for the potential development of "pathway-specific" selective ER modulators.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estrogen receptor alpha and endothelial nitric oxide synthase are organized into a functional signaling module in caveolae.Circ Res. 2000 Nov 24;87(11):E44-52. doi: 10.1161/01.res.87.11.e44. Circ Res. 2000. PMID: 11090554
-
Estrogen receptor alpha mediates the nongenomic activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by estrogen.J Clin Invest. 1999 Feb;103(3):401-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI5347. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 9927501 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone's rapid, nongenomic effects are mediated by striatin: a modulator of aldosterone's effect on estrogen action.Endocrinology. 2014 Jun;155(6):2233-43. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1834. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24654783 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen modulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.Endocr Rev. 2002 Oct;23(5):665-86. doi: 10.1210/er.2001-0045. Endocr Rev. 2002. PMID: 12372846 Review.
-
Rapid activation of endothelial NO synthase by estrogen: evidence for a steroid receptor fast-action complex (SRFC) in caveolae.Steroids. 2002 May;67(6):413-9. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(01)00177-5. Steroids. 2002. PMID: 11960616 Review.
Cited by
-
ER Alpha Rapid Signaling Is Required for Estrogen Induced Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Endothelial Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 1;11(4):e0152807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152807. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27035664 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of alternative splicing as a potential regulator in fat-tail development of sheep: a comprehensive RNA-seq based study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 29;14(1):2361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52855-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38287039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oestradiol as a neuromodulator of learning and memory.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Oct;21(10):535-550. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0362-7. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32879508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional analysis of the PP2A subfamily of protein phosphatases in regulating Drosophila S6 kinase.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Aug 15;313(14):3117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.05.008. Epub 2007 May 16. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17570358 Free PMC article.
-
Loading-related regulation of gene expression in bone in the contexts of estrogen deficiency, lack of estrogen receptor alpha and disuse.Bone. 2010 Mar;46(3):628-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.10.021. Epub 2009 Oct 24. Bone. 2010. PMID: 19857613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendelsohn, M. E. & Karas, R. H. (1999) N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 1801–1811. - PubMed
-
- Chambliss, K. L., Yuhanna, I. S., Anderson, R. G., Mendelsohn, M. E. & Shaul, P. W. (2002) Mol. Endocrinol. 16, 938–946. - PubMed
-
- Chambliss, K. L., Yuhannna, I. S., Mineo, C., Liu, C., German, Z., Sherman, T. S., Mendelsohn, M. E., Anderson, R. G. W. & Shaul, P. W. (2000) Circ. Res. E44–E52. - PubMed
-
- Haynes, M. P., Sinha, D., Strong Russell, K., Collinge, M., Fulton D, MoralesRuiz, M. & Bender, J. R. (2000) Circ. Res. 87, 677–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

