Bactericidal effects of toluidine blue-mediated photodynamic action on Vibrio vulnificus
- PMID: 15728881
- PMCID: PMC549273
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.3.895-902.2005
Bactericidal effects of toluidine blue-mediated photodynamic action on Vibrio vulnificus
Abstract
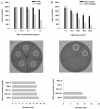
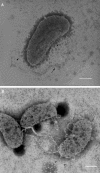
Vibrio vulnificus is a gram-negative, highly invasive bacterium responsible for human opportunistic infections. We studied the antibacterial effects of toluidine blue O (TBO)-mediated photodynamic therapy (PDT) for V. vulnificus wound infections in mice. Fifty-three percent (10 of 19) of mice treated with 100 microg of TBO per ml and exposed to broad-spectrum red light (150 J/cm(2) at 80 mW/cm(2)) survived, even though systemic septicemia had been established with a bacterial inoculum 100 times the 50% lethal dose. In vitro, the bacteria were killed after exposure to a lower light dose (100 J/cm(2) at 80 mW/cm(2)) in the presence of low-dose TBO (0.1 microg/ml). PDT severely damaged the cell wall and reduced cell motility and virulence. Cell-killing effects were dependent on the TBO concentration and light doses and were mediated partly through the reactive oxygen species generated during the photodynamic reaction. Our study has demonstrated that PDT can cure mice with otherwise fatal V. vulnificus wound infections. These promising results suggest the potential of this regimen as a possible alternative to antibiotics in future clinical applications.
Figures
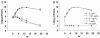

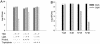
Similar articles
-
Photodynamic effects of toluidine blue on human oral keratinocytes and fibroblasts and Streptococcus sanguis evaluated in vitro.Lasers Surg Med. 1996;18(3):253-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9101(1996)18:3<253::AID-LSM6>3.0.CO;2-R. Lasers Surg Med. 1996. PMID: 8778520
-
Toluidine blue O photodynamic inactivation on multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Lasers Surg Med. 2009 Jul;41(5):391-7. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20765. Lasers Surg Med. 2009. PMID: 19533759
-
Use of a marker plasmid to examine differential rates of growth and death between clinical and environmental strains of Vibrio vulnificus in experimentally infected mice.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Jul;61(2):310-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05227.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16856938
-
Vibrio vulnificus infection: diagnosis and treatment.Am Fam Physician. 2007 Aug 15;76(4):539-44. Am Fam Physician. 2007. PMID: 17853628 Review.
-
Molecular Pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:118-31. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765065 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage-_targeted nanoparticles mediate synergistic photodynamic therapy and immunotherapy of tuberculosis.RSC Adv. 2023 Jan 11;13(3):1727-1737. doi: 10.1039/d2ra06334d. eCollection 2023 Jan 6. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36712647 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic therapy induces an immune response against a bacterial pathogen.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012 Jul;8(5):479-94. doi: 10.1586/eci.12.37. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22882222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Blue Light for Prevention and Treatment of Highly Invasive Vibrio vulnificus Burn Infection in Mice.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 12;13:932466. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.932466. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35903474 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps potentiate antimicrobial photoinactivation.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Sep;52(9):3202-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00006-08. Epub 2008 May 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18474586 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy treatment of chronic recurrent sinusitis biofilms.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011 Sep-Oct;1(5):329-34. doi: 10.1002/alr.20089. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011. PMID: 22287461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alia, P. Mohanty, and J. Matysik. 2001. Effect of proline on the production of singlet oxygen. Amino Acids 21:195-200. - PubMed
-
- Arnfield, M., S. Gonzalez, P. Lea, J. Tulip, and M. McPhee. 1986. Cylindrical irradiator fiber tip for photodynamic therapy. Lasers Surg. Med. 6:150-154. - PubMed
-
- Bhatti, M., A. MacRobert, S. Meghji, B. Henderson, and M. Wilson. 1998. A study of the uptake of toluidine blue O by Porphyromonas gingivalis and the mechanism of lethal photosensitization. Photochem. Photobiol. 68:370-376. - PubMed
-
- Blake, P. A., M. H. Merson, R. E. Weaver, D. G. Hollis, and P. C. Heublein. 1979. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N. Engl. J. Med. 300:1-5. - PubMed
-
- Burger, M., R. G. Woods, C. McCarthy, and I. R. Beacham. 2000. Temperature regulation of protease in Pseudomonas fluorescens LS107d2 by an ECF sigma factor and a transmembrane activator. Microbiology 146:3149-3155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

