Mitochondrial energy metabolism in heart failure: a question of balance
- PMID: 15765136
- PMCID: PMC1052011
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI24405
Mitochondrial energy metabolism in heart failure: a question of balance
Abstract
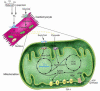
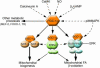
The mitochondrion serves a critical role as a platform for energy transduction, signaling, and cell death pathways relevant to common diseases of the myocardium such as heart failure. This review focuses on the molecular regulatory events and downstream effector pathways involved in mitochondrial energy metabolic derangements known to occur during the development of heart failure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The PPAR regulatory system in cardiac physiology and disease.Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Jan 15;73(2):269-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.08.023. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17010956 Review.
-
Nuclear receptor signaling and cardiac energetics.Circ Res. 2004 Sep 17;95(6):568-78. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000141774.29937.e3. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15375023 Review.
-
Estrogen-related receptor alpha directs peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha signaling in the transcriptional control of energy metabolism in cardiac and skeletal muscle.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Oct;24(20):9079-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.9079-9091.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15456881 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 (PGC-1) regulatory cascade in cardiac physiology and disease.Circulation. 2007 May 15;115(19):2540-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.670588. Circulation. 2007. PMID: 17502589 No abstract available.
-
Evidence for a mitochondrial regulatory pathway defined by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 alpha, estrogen-related receptor-alpha, and mitofusin 2.Diabetes. 2006 Jun;55(6):1783-91. doi: 10.2337/db05-0509. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16731843
Cited by
-
NAD+ precursors prolong survival and improve cardiac phenotypes in a mouse model of Friedreich's Ataxia.JCI Insight. 2024 Jul 18;9(16):e177152. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.177152. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39171530 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure of the inner mitochondrial membrane triggers apoptotic mitophagy.Cell Death Differ. 2024 Mar;31(3):335-347. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01260-2. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Cell Death Differ. 2024. PMID: 38396150 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-Blockers of Different Generations: Features of Influence on the Disturbances of Myocardial Energy Metabolism in Doxorubicin-Induced Chronic Heart Failure in Rats.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 28;12(9):1957. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12091957. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335471 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced alteration of mitochondrial genes in cardiomyocytes: role of Bnip3 and Pdk1.Shock. 2010 Aug;34(2):169-75. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181cffe7d. Shock. 2010. PMID: 20160671 Free PMC article.
-
Transverse aortic constriction leads to accelerated heart failure in mice lacking PPAR-gamma coactivator 1alpha.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 27;103(26):10086-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603615103. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16775082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stanley WC, Chandler MP. Energy metabolism in the normal and failing heart: potential for therapeutic interventions. Heart Fail. Rev. 2002;7:115–130. - PubMed
-
- Taegtmeyer H. Energy metabolism of the heart: from basic concepts to clinical applications. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 1994;19:59–113. - PubMed
-
- Bing RJ, Siegel A, Ungar I, Gilbert M. Metabolism of the human heart. II. Studies on fat, ketone and amino acid metabolism. Am. J. Med. 1954;16:504–515. - PubMed
-
- Shipp JC, Opie LH, Challoner D. Fatty acid and glucose metabolism in the perfused heart. Nature. 1961;189:1018–1019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL058493/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60-DK20579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK45416/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK045416/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01-DK063051/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK52574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL58493/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK063051/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL57278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

