Trends in the prevalence and management of diagnosed type 2 diabetes 1994-2001 in England and Wales
- PMID: 15784133
- PMCID: PMC1079812
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2296-6-13
Trends in the prevalence and management of diagnosed type 2 diabetes 1994-2001 in England and Wales
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes is an important cause of morbidity and mortality. Its prevalence appears to be increasing. Guidelines exist regarding its management. Recommendations regarding drug therapy have changed. Little is known about the influence of these guidelines and changed recommendations on the actual management of patients with type 2 diabetes. This study aims to document trends in the prevalence, drug treatment and recording of measures related to the management of type 2 diabetes; and to assess whether recommended _targets can be met.
Methods: The population comprised subjects registered between 1994 and 2001 with 74 general practices in England and Wales which routinely contribute to the Doctors' Independent Network database. Approximately 500,000 patients and 10,000 type 2 diabetics were registered in each year.
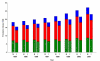
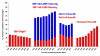
Results: Type 2 diabetes prevalence rose from 17/1000 in 1994 to 25/1000 in 2001. Drug therapy has changed: use of long acting sulphonylureas is falling while that of short acting sulphonylureas, metformin and newer therapies including glitazones is increasing. Electronic recording of HbA1c, blood pressure, cholesterol and weight have risen steadily, and improvements in control of blood pressure and cholesterol levels have occurred. However, glycaemic control has not improved, and obesity has increased. The percentage with a BMI under 25 kg/m2 fell from 27.0% in 1994 to 19.4% in 2001 (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing. Its primary care management has changed in accordance with best evidence. Monitoring has improved, but further improvement is possible. Despite this, glycaemic control has not improved, while the prevalence of obesity in the diabetic population is rising.
Figures

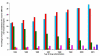
Similar articles
-
Patterns of anti-diabetic medication use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in England and Wales.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2017 Feb;26(2):127-135. doi: 10.1002/pds.4092. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 27642000
-
Metformin-pioglitazone and metformin-rosiglitazone effects on non-conventional cardiovascular risk factors plasma level in type 2 diabetic patients with metabolic syndrome.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2006 Aug;31(4):375-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2006.00756.x. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2006. PMID: 16882108 Clinical Trial.
-
[Prevalence of diabetes, antidiabetic treatment and chronic diabetic complications reported by general practitioners].Przegl Lek. 2005;62(4):201-5. Przegl Lek. 2005. PMID: 16229234 Polish.
-
Newer agents for blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jul;14(36):1-248. doi: 10.3310/hta14360. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20646668 Review.
-
Dapagliflozin compared with other oral anti-diabetes treatments when added to metformin monotherapy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 May;16(5):433-42. doi: 10.1111/dom.12239. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 24237939 Review.
Cited by
-
Letter to the editor: alarming prevalence of comorbid conditions in adults with type 2 diabetes in Iran.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Jul 14;22(2):1809-1811. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01254-w. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 37975112 Free PMC article.
-
Non-alcohol fatty liver disease in Asia: Prevention and planning.World J Hepatol. 2015 Jul 8;7(13):1788-96. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i13.1788. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26167252 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of new insights and revised practice guidelines on prescribing drugs in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes mellitus.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;62(6):660-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02711.x. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16796700 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic implications of curcumin in the prevention of diabetic retinopathy via modulation of anti-oxidant activity and genetic pathways.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 15;5(4):194-202. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24379904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time trend analysis of the prevalence and incidence of diagnosed type 2 diabetes among adults in Taiwan from 2000 to 2007: a population-based study.BMC Public Health. 2013 Apr 9;13:318. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-318. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23570503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Newnham A, Ryan R, Khunti K, Majeed A. Prevalence of diagnosed diabetes mellitus in general practice in England and Wales, 1994 to 1998. Health Statistics Quarterly. 2002;14:5–13.
-
- Excellence NIC. Management of Type 2 Diabetes - management of blood pressure and blood lipids (Guideline H) http://www nice org uk/pdf/NICE_INHERITEd_Hv8 pdf. 2002. http://www.nice.org.uk/pdf/NICE_INHERITEd_Hv8.pdf
-
- Excellence NIC. Management of type 2 diabetes – Managing blood glucose levels (Guideline G) http://www nice org uk/pdf/NICE_INHERITEG_guidelines pdf. 2002. http://www.nice.org.uk/pdf/NICE_INHERITEG_guidelines.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

