Ubp10/Dot4p regulates the persistence of ubiquitinated histone H2B: distinct roles in telomeric silencing and general chromatin
- PMID: 15988024
- PMCID: PMC1168808
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.14.6123-6139.2005
Ubp10/Dot4p regulates the persistence of ubiquitinated histone H2B: distinct roles in telomeric silencing and general chromatin
Abstract
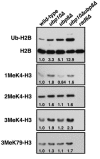
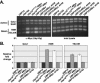
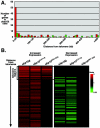
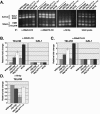
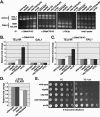
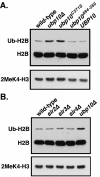
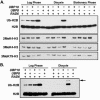
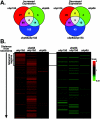
We previously discovered that the ubiquitin protease Ubp10/Dot4p is important for telomeric silencing through its interaction with Sir4p. However, the mechanism of Ubp10p action was unknown. We now provide evidence that Ubp10p removes ubiquitin from histone H2B; cells with UBP10 deleted have increased steady-state levels of H2B ubiquitination. As a consequence, ubp10delta cells also have increased steady-state levels of histone H3 Lys4 and Lys79 methylation. Consistent with its role in silencing, Ubp10p is preferentially localized to silent chromatin where its ubiquitin protease activity maintains low levels of H3 Lys4 and Lys79 methylation to allow optimal Sir protein binding to telomeres and global telomeric silencing. The ubiquitin protease Ubp8p has also been shown to remove ubiquitin from H2B, and ubp8delta cells have increased steady-state levels of H2B ubiquitination similar to those in ubp10delta cells. Unlike ubp10delta cells, however, ubp8delta cells do not have increased steady-state levels of H3 Lys4 and Lys79 methylation, nor is telomeric silencing affected. Despite their separate functions in silencing and SAGA-mediated transcription, respectively, deletion of both UBP10 and UBP8 results in a synergistic increase in the steady-state levels of H2B ubiquitination and in the number of genes with altered expression, indicating that Ubp10p and Ubp8p likely overlap in some of their _target chromatin regions. We propose that Ubp10p and Ubp8p are the only ubiquitin proteases that normally remove monoubiquitin from histone H2B and, while there are regions of the genome to which each is specifically _targeted, both combine to regulate the global balance of H2B ubiquitination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maintenance of low histone ubiquitylation by Ubp10 correlates with telomere-proximal Sir2 association and gene silencing.Mol Cell. 2005 Feb 18;17(4):585-94. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.01.007. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15721261
-
The Rtf1 component of the Paf1 transcriptional elongation complex is required for ubiquitination of histone H2B.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 5;278(36):33625-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C300270200. Epub 2003 Jul 21. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12876293
-
Histone chaperone Chz1p regulates H2B ubiquitination and subtelomeric anti-silencing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Mar;38(5):1431-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1099. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20008511 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay of histone H2B ubiquitination with budding and fission yeast heterochromatin.Curr Genet. 2018 Aug;64(4):799-806. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0812-1. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29464330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone post-translational modifications regulate transcription and silent chromatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop. 2006;(57):127-53. doi: 10.1007/3-540-37633-x_8. Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop. 2006. PMID: 16568953 Review.
Cited by
-
DET1-mediated degradation of a SAGA-like deubiquitination module controls H2Bub homeostasis.Elife. 2018 Sep 7;7:e37892. doi: 10.7554/eLife.37892. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30192741 Free PMC article.
-
A histone H2A deubiquitinase complex coordinating histone acetylation and H1 dissociation in transcriptional regulation.Mol Cell. 2007 Aug 17;27(4):609-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.024. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17707232 Free PMC article.
-
Rad6-Bre1-mediated H2B ubiquitination regulates telomere replication by promoting telomere-end resection.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Apr 7;45(6):3308-3322. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx101. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28180293 Free PMC article.
-
USP49 deubiquitinates histone H2B and regulates cotranscriptional pre-mRNA splicing.Genes Dev. 2013 Jul 15;27(14):1581-95. doi: 10.1101/gad.211037.112. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23824326 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H2B ubiquitylation: Connections to transcription and effects on chromatin structure.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2024 Jun;1867(2):195018. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2024.195018. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2024. PMID: 38331024 Review.
References
-
- Ai, W., P. G. Bertram, C. K. Tsang, T. F. Chan, and X. F. Zheng. 2002. Regulation of subtelomeric silencing during stress response. Mol. Cell 10:1295-1305. - PubMed
-
- Amerik, A. Y., S. J. Li, and M. Hochstrasser. 2000. Analysis of the deubiquitinating enzymes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biol. Chem. 381:981-992. - PubMed
-
- Baldi, P., and A. D. Long. 2001. A Bayesian framework for the analysis of microarray expression data: regularized t-test and statistical inferences of gene changes. Bioinformatics 17:509-519. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini, Y., and Y. Hochberg. 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 57:289-300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
