Feed-forward inhibition: a novel cellular mechanism for the analgesic effect of substance P
- PMID: 16297242
- PMCID: PMC1315348
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-1-34
Feed-forward inhibition: a novel cellular mechanism for the analgesic effect of substance P
Abstract
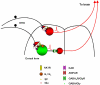
Substance P (SP) is a neuropeptide well known for its contribution to pain transmission in the spinal cord, however, less is known about the possible modulatory effects of SP. A new study by Gu and colleagues, published in Molecular Pain (2005, 1:20), describes its potential role in feed-forward inhibition in lamina V of the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. This inhibition seems to function through a direct excitation of GABAergic interneurons by substance P released from primary afferent fibers and has a distinct temporal phase of action from the well-described glutamate-dependent feed-forward inhibition. It is believed that through this inhibition, substance P can balance nociceptive output from the spinal cord.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased nociceptive input rapidly modulates spinal GABAergic transmission through endogenously released glutamate.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Jan;97(1):871-82. doi: 10.1152/jn.00964.2006. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17108089
-
Hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel subunit 2 ion channels modulate synaptic transmission from nociceptive primary afferents containing substance P to secondary sensory neurons in laminae I-IIo of the rodent spinal dorsal horn.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Sep;24(5):1341-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05013.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16987220
-
Ionotropic glutamate receptors are expressed in GABAergic terminals in the rat superficial dorsal horn.J Comp Neurol. 2005 May 30;486(2):169-78. doi: 10.1002/cne.20525. J Comp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15844209
-
[Analgesic mechanisms of noradrenaline in the spinal dorsal horn].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2001 Jul;32(3):225-8. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2001. PMID: 12545794 Review. Chinese.
-
The role of peptides in central sensitization.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(194):451-91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79090-7_13. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19655115 Review.
Cited by
-
AAV-Mediated Combination Gene Therapy for Neuropathic Pain: GAD65, GDNF, and IL-10.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Jun 25;18:473-483. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.018. eCollection 2020 Sep 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 32728596 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Channels Involved in Substance P-Mediated Nociception and Antinociception.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 30;20(7):1596. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071596. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30935032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Periodontal Health and Its Relationship with Psychological Stress: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Clin Med. 2024 May 16;13(10):2942. doi: 10.3390/jcm13102942. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38792482 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep-inducing effect of substance P-cholera toxin A subunit in mice.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Oct 17;659:44-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.066. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28866052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoshimura M, Jessell TM. Primary afferent-evoked synaptic responses and slow potential generation in rat substantia gelatinosa neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1989;62:96–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

