Peroxidase activity and structural transitions of cytochrome c bound to cardiolipin-containing membranes
- PMID: 16605268
- PMCID: PMC2527545
- DOI: 10.1021/bi0525573
Peroxidase activity and structural transitions of cytochrome c bound to cardiolipin-containing membranes
Abstract
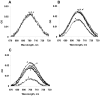
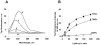
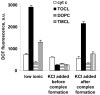
During apoptosis, cytochrome c (cyt c) is released from intermembrane space of mitochondria into the cytosol where it triggers the caspase-dependent machinery. We discovered that cyt c plays another critical role in early apoptosis as a cardiolipin (CL)-specific oxygenase to produce CL hydroperoxides required for release of pro-apoptotic factors [Kagan, V. E., et al. (2005) Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 223-232]. We quantitatively characterized the activation of peroxidase activity of cyt c by CL and hydrogen peroxide. At low ionic strength and high CL/cyt c ratios, peroxidase activity of the CL/cyt c complex was increased >50 times. This catalytic activity correlated with partial unfolding of cyt c monitored by Trp(59) fluorescence and absorbance at 695 nm (Fe-S(Met(80)) band). The peroxidase activity increase preceded the loss of protein tertiary structure. Monounsaturated tetraoleoyl-CL (TOCL) induced peroxidase activity and unfolding of cyt c more effectively than saturated tetramyristoyl-CL (TMCL). TOCL/cyt c complex was found more resistant to dissociation by high salt concentration. These findings suggest that electrostatic CL/cyt c interactions are central to the initiation of the peroxidase activity, while hydrophobic interactions are involved when cyt c's tertiary structure is lost. In the presence of CL, cyt c peroxidase activity is activated at lower H(2)O(2) concentrations than for isolated cyt c molecules. This suggests that redistribution of CL in the mitochondrial membranes combined with increased production of H(2)O(2) can switch on the peroxidase activity of cyt c and CL oxidation in mitochondria-a required step in execution of apoptosis.
Figures
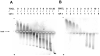



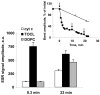
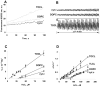
Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms for the induction of peroxidase activity of the cytochrome c-cardiolipin complex.Biochemistry. 2011 Oct 4;50(39):8383-91. doi: 10.1021/bi2010202. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21877718
-
Nitric oxide inhibits peroxidase activity of cytochrome c.cardiolipin complex and blocks cardiolipin oxidation.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 26;281(21):14554-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509507200. Epub 2006 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16543234
-
The hierarchy of structural transitions induced in cytochrome c by anionic phospholipids determines its peroxidase activation and selective peroxidation during apoptosis in cells.Biochemistry. 2007 Dec 11;46(49):14232-44. doi: 10.1021/bi701237b. Epub 2007 Nov 16. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 18004876
-
The "pro-apoptotic genies" get out of mitochondria: oxidative lipidomics and redox activity of cytochrome c/cardiolipin complexes.Chem Biol Interact. 2006 Oct 27;163(1-2):15-28. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2006.04.019. Epub 2006 May 12. Chem Biol Interact. 2006. PMID: 16797512 Review.
-
Apoptotic interactions of cytochrome c: redox flirting with anionic phospholipids within and outside of mitochondria.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 May-Jun;1757(5-6):648-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.03.002. Epub 2006 Mar 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16740248 Review.
Cited by
-
Spin cascade and doming in ferric hemes: Femtosecond X-ray absorption and X-ray emission studies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):21914-21920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009490117. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32848065 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiolipin signaling mechanisms: collapse of asymmetry and oxidation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Jun 20;22(18):1667-80. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6219. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 25566681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subtle Change in the Charge Distribution of Surface Residues May Affect the Secondary Functions of Cytochrome c.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 5;290(23):14476-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.607010. Epub 2015 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25873393 Free PMC article.
-
Suitability of Adenosine Derivatives in Improving the Activity and Stability of Cytochrome c under Stress: Insights into the Effect of Phosphate Groups.J Phys Chem B. 2024 Jan 11;128(1):86-95. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c05996. Epub 2023 Dec 21. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 38127495 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiolipin switch in mitochondria: shutting off the reduction of cytochrome c and turning on the peroxidase activity.Biochemistry. 2007 Mar 20;46(11):3423-34. doi: 10.1021/bi061854k. Epub 2007 Feb 24. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17319652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cecconi C, Shank EA, Bustamante C, Marqusee S. Direct observation of the three-state folding of a single protein molecule. Science. 2005;309:2057–60. - PubMed
-
- Pettigrew GW, Moore GR. Cytochrome c - Biological aspects. Springer-Verlaf; Berlin. Heidelberg: 1987.
-
- Bushnell GW, Louie GV, Brayer GD. High-resolution three-dimensional structure of horse heart cytochrome c. J Mol Biol. 1990;214:585–95. - PubMed
-
- McMillin JB, Dowhan W. Cardiolipin and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1585:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Jori G, Tamburro AM, Azzi A. Photooxidative and spectral studies on cytochrome c. Conformational changes induced by binding of cardiolipin. Photochem Photobiol. 1974;19:337–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

