Myc influences global chromatin structure
- PMID: 16724113
- PMCID: PMC1500848
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601152
Myc influences global chromatin structure
Abstract
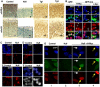
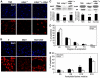
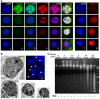
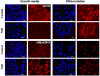
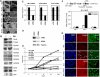
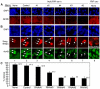
The family of myc proto-oncogenes encodes transcription factors (c-, N-, and L-Myc) that regulate cell growth and proliferation and are involved in the etiology of diverse cancers. Myc proteins are thought to function by binding and regulating specific _target genes. Here we report that Myc proteins are required for the widespread maintenance of active chromatin. Disruption of N-myc in neuronal progenitors and other cell types leads to nuclear condensation accompanied by large-scale changes in histone modifications associated with chromatin inactivation, including hypoacetylation and altered methylation. These effects are largely reversed by exogenous Myc as well as by differentiation and are mimicked by the Myc antagonist Mad1. The first chromatin changes are evident within 6 h of Myc loss and lead to changes in chromatin structure. Myc widely influences chromatin in part through upregulation of the histone acetyltransferase GCN5. This study provides the first evidence for regulation of global chromatin structure by an oncoprotein and may explain the broad effects of Myc on cell behavior and tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual regulation of c-Myc by p300 via acetylation-dependent control of Myc protein turnover and coactivation of Myc-induced transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(23):10220-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10220-10234.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16287840 Free PMC article.
-
MYC interacts with the human STAGA coactivator complex via multivalent contacts with the GCN5 and TRRAP subunits.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1839(5):395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24705139 Free PMC article.
-
MYC recruits the TIP60 histone acetyltransferase complex to chromatin.EMBO Rep. 2003 Jun;4(6):575-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor861. EMBO Rep. 2003. PMID: 12776177 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct GCN5/PCAF-containing complexes function as co-activators and are involved in transcription factor and global histone acetylation.Oncogene. 2007 Aug 13;26(37):5341-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210604. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17694077 Review.
-
Chromatin remodeling and transcription.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997 Apr;7(2):182-91. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(97)80127-x. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997. PMID: 9115421 Review.
Cited by
-
The SAGA acetyltransferase module is required for the maintenance of MAF and MYC oncogenic gene expression programs in multiple myeloma.Genes Dev. 2024 Sep 19;38(15-16):738-754. doi: 10.1101/gad.351789.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 39168636 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor cell-selective regulation of NOXA by c-MYC in response to proteasome inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 4;104(49):19488-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708380104. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18042711 Free PMC article.
-
MYC deregulates TET1 and TET2 expression to control global DNA (hydroxy)methylation and gene expression to maintain a neoplastic phenotype in T-ALL.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019 Jul 2;12(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13072-019-0278-5. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019. PMID: 31266538 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional foundation of pluripotency.Development. 2009 Jul;136(14):2311-22. doi: 10.1242/dev.024398. Development. 2009. PMID: 19542351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential regulation of N-Myc and c-Myc synthesis, degradation, and transcriptional activity by the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 4;286(44):38498-38508. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.276675. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21908617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410 - PubMed
-
- Arabi A, Wu S, Ridderstrale K, Bierhoff H, Shiue C, Fatyol K, Fahlen S, Hydbring P, Soderberg O, Grummt I, Larsson LG, Wright AP (2005) c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat Cell Biol 7: 303–310 - PubMed
-
- Aruga J, Yokota N, Hashimoto M, Furuichi T, Fukuda M, Mikoshiba K (1994) A novel zinc finger protein, zic, is involved in neurogenesis, especially in the cell lineage of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem 63: 1880–1890 - PubMed
-
- Ayer DE (1999) Histone deacetylases: transcriptional repression with siners and nurds. Trends Cell Biol 9: 193–198 - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

