Classification and natural history of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
- PMID: 16738191
- PMCID: PMC2658683
- DOI: 10.1513/pats.200601-005TK
Classification and natural history of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
Abstract
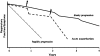
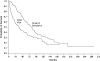
In the American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society consensus classification, idiopathic interstitial pneumonias are classified into seven clinicopathologic entities. The classification is largely based on histopathology, but depends on the close interaction of clinician, radiologist, and pathologist. An accurate diagnosis can be very difficult, especially when deciding between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; better diagnostic markers are needed. The prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is very poor, with median survival of 2-4 yr after the diagnosis, yet the course of individual patients is highly variable. Predicting prognosis in the individual patient is challenging but various clinical and radiologic variables have been identified. According to several recent clinical trials, the natural history of this disease may involve periods of relative stability punctuated by acute exacerbations of disease that result in substantial morbidity or death. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is characterized by a distinct histopathologic appearance and a better prognosis than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. However, there is still confusion and controversy over the relationship between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Diffuse idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. International multidisciplinary consensus classification by the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society, principal clinico-pathological entities, and diagnosis].Rev Mal Respir. 2004 Apr;21(2 Pt 1):299-318. doi: 10.1016/s0761-8425(04)71288-7. Rev Mal Respir. 2004. PMID: 15211238 Review. French.
-
[Idiopathic diffuse interstitial lung disease].Rev Prat. 2000 Nov 1;50(17):1901-5. Rev Prat. 2000. PMID: 11151331 Review. French.
-
Historical perspective: a pathologic approach to the classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias.Chest. 2005 Nov;128(5 Suppl 1):513S-519S. doi: 10.1378/chest.128.5_suppl_1.513S. Chest. 2005. PMID: 16304241 Review.
-
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: a re-appraisal of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001 Dec;5(12):1086-98. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001. PMID: 11769766 Review.
-
[Histological classification of interstitial lung diseases].Z Rheumatol. 2003 Feb;62(1):16-20. doi: 10.1007/s00393-003-0476-0. Z Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 12624798 Free PMC article. Review. German.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic approach to interstitial pneumonias in a single centre: report on 88 cases.Diagn Pathol. 2012 Nov 26;7:160. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-160. Diagn Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23181688 Free PMC article.
-
Lung transplant for interstitial lung disease: outcomes for single versus bilateral lung transplantation.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012 Mar;14(3):263-7. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivr085. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012. PMID: 22180607 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of the prognostic model based on autophagy-associated genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 12;13:1049361. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1049361. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36578501 Free PMC article.
-
Age and sex dimorphisms contribute to the severity of bleomycin-induced lung injury and fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):L510-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00122.2011. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21743030 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic signature for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis based on five-immune-related genes.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(20):1570. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4545. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34790776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liebow AA, Carrington DB. The interstitial pneumonias. In: Simon M, Potchen EJ, LeMay M, editors. Frontiers of pulmonary radiology. New York: Grune & Stratteon; 1969. pp. 102–141.
-
- Katzenstein ALA, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:1301–1315. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Flaherty KR, King TE Jr, Raghu G, Lynch JP III, Colby TV, Travis WD, Gross BH, Kazerooni EA, Toews GB, Long Q, et al. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: what is the effect of a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;170:904–910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
