TBP is differentially regulated by c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) and JNK2 through Elk-1, controlling c-Jun expression and cell proliferation
- PMID: 17074809
- PMCID: PMC1800663
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01365-06
TBP is differentially regulated by c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) and JNK2 through Elk-1, controlling c-Jun expression and cell proliferation
Abstract
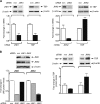
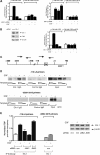
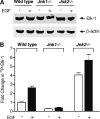
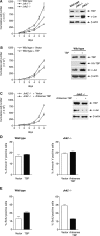
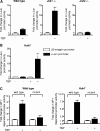
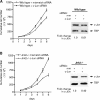
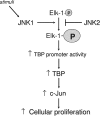
Emerging evidence supports the idea that the c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) possess overlapping but distinct functions. The potential roles of the ubiquitously expressed JNK1 and JNK2 in regulating expression of the central transcription initiation factor, TATA-binding protein (TBP), were examined. Relative to wild-type fibroblasts, TBP was decreased in Jnk1(-/-) cells and increased in Jnk2(-/-) cells. Similarly, reduction of JNK1 in human hepatoma cells decreased TBP expression, whereas reduction of JNK2 enhanced it. JNK-mediated regulation of TBP expression occurs at the transcriptional level through their ability to _target Elk-1, which directly regulates the TBP promoter in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation. JNK1 increases, whereas JNK2 decreases, the phosphorylation state of Elk-1, which differentially affects Elk-1 occupancy at a defined site within the TBP promoter. These JNK-mediated alterations in TBP expression, alone, serve to regulate c-Jun expression and fibroblast proliferation rates. These studies uncovered several new molecular events that distinguish the functions of JNK1 and JNK2 that are critical for their regulation of cellular proliferation.
Figures
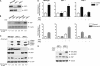
Similar articles
-
The JNKs differentially regulate RNA polymerase III transcription by coordinately modulating the expression of all TFIIIB subunits.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 4;106(31):12682-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904843106. Epub 2009 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19620725 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase 1 (JNK1), but not JNK2, is essential for tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced c-Jun kinase activation and apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;24(24):10844-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10844-10856.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15572687 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles for JNK1 and JNK2 in regulating JNK activity and c-Jun-dependent cell proliferation.Mol Cell. 2004 Sep 10;15(5):713-25. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.028. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15350216
-
JNK2: a negative regulator of cellular proliferation.Cell Cycle. 2004 Dec;3(12):1520-3. doi: 10.4161/cc.3.12.1315. Epub 2004 Dec 18. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15611655 Review.
-
c-Jun and the transcriptional control of neuronal apoptosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1015-21. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00372-5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007936 Review.
Cited by
-
An Elk transcription factor is required for Runx-dependent survival signaling in the sea urchin embryo.Dev Biol. 2016 Aug 1;416(1):173-186. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.05.026. Epub 2016 May 24. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27235147 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role and Mechanism of pAMPKα-Mediated Dysregulation of Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 20;2021:5554932. doi: 10.1155/2021/5554932. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33995823 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Tumor Characteristics of Patients with High Serum Levels of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;13(19):4842. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194842. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638326 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription is required for oncogenic transformation.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 11;283(28):19184-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802872200. Epub 2008 May 1. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18456653 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 (JNK2) antagonizes the signaling of differentiation by JNK1 in human myeloid leukemia cells resistant to vitamin D.Leuk Res. 2009 Oct;33(10):1372-8. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.03.003. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Leuk Res. 2009. PMID: 19339050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang, L., Y. Jones, M. H. Ellisman, L. S. Goldstein, and M. Karin. 2003. JNK1 is required for maintenance of neuronal microtubules and controls phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins. Dev. Cell 4:521-533. - PubMed
-
- Chang, L., and M. Karin. 2001. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410:37-40. - PubMed
-
- Choi, B. Y., H. S. Choi, K. Ko, Y. Cho, F. Zhu, B. S. Kang, S. P. Ermakova, W. Y. Ma, A. M. Bode, and Z. Dong. 2005. The tumor suppressor p16(INK4a) prevents cell transformation through inhibition of c-Jun phosphorylation and AP-1 activity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12:699-707. - PubMed
-
- Colgan, J., and J. L. Manley. 1992. TFIID can be rate limiting in vivo for TATA-containing but not TATA-lacking, RNA pol II promoters. Genes Dev. 6:304-315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
