Amyloid-beta-induced pathological behaviors are suppressed by Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 and ginkgolides in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 17167099
- PMCID: PMC6674971
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3448-06.2006
Amyloid-beta-induced pathological behaviors are suppressed by Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 and ginkgolides in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
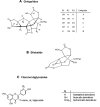
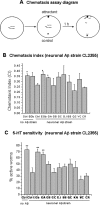
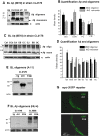
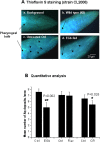
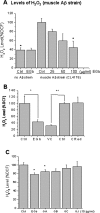
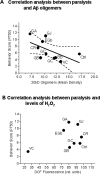
Amyloid-beta (Abeta) toxicity has been postulated to initiate synaptic loss and subsequent neuronal degeneration seen in Alzheimer's disease (AD). We previously demonstrated that the standardized Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761, commonly used to enhance memory and by AD patients for dementia, inhibits Abeta-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. In this study, we use EGb 761 and its single constituents to associate Abeta species with Abeta-induced pathological behaviors in a model organism, Caenorhabditis elegans. We report that EGb 761 and one of its components, ginkgolide A, alleviates Abeta-induced pathological behaviors, including paralysis, and reduces chemotaxis behavior and 5-HT hypersensitivity in a transgenic C. elegans. We also show that EGb 761 inhibits Abeta oligomerization and Abeta deposits in the worms. Moreover, reducing oxidative stress is not the mechanism by which EGb 761 and ginkgolide A suppress Abeta-induced paralysis because the antioxidant L-ascorbic acid reduced intracellular levels of hydrogen peroxide to the same extent as EGb 761, but was not nearly as effective in suppressing paralysis in the transgenic C. elegans. These findings suggest that (1) EGb 761 suppresses Abeta-related pathological behaviors, (2) the protection against Abeta toxicity by EGb 761 is mediated primarily by modulating Abeta oligomeric species, and (3) ginkgolide A has therapeutic potential for prevention and treatment of AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heat shock treatment reduces beta amyloid toxicity in vivo by diminishing oligomers.Neurobiol Aging. 2010 Jun;31(6):1055-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.07.013. Epub 2008 Aug 30. Neurobiol Aging. 2010. PMID: 18762355 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease, the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, and ginkgo biloba leaf extract.Life Sci. 2006 Mar 27;78(18):2066-72. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.12.004. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16507312 Review.
-
Elevation of oxidative free radicals in Alzheimer's disease models can be attenuated by Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761.J Alzheimers Dis. 2003 Aug;5(4):287-300. doi: 10.3233/jad-2003-5404. J Alzheimers Dis. 2003. PMID: 14624024
-
The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by beta-amyloid.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Jun;12(6):1882-90. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00069.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10886329
-
Pharmacological studies supporting the therapeutic use of Ginkgo biloba extract for Alzheimer's disease.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003 Jun;36 Suppl 1:S8-14. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40454. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 13130383 Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of Alzheimer's Disease and Some Therapeutic Approaches _targeting Aβ by Using Several Synthetic and Herbal Compounds.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:7361613. doi: 10.1155/2016/7361613. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27034741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Analyses of Metal Responsive Genes in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Genet. 2012 Apr 10;3:52. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00052. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 22514555 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin Attenuates Aβ Pathology Mediated Through Levamisole Sensitive Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in a C. elegans Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Sep;54(7):5427-5439. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0085-y. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27596506
-
Natural Bioactive Products and Alzheimer's Disease Pathology: Lessons from Caenorhabditis elegans Transgenic Models.Diseases. 2022 May 13;10(2):28. doi: 10.3390/diseases10020028. Diseases. 2022. PMID: 35645249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor functions as a regulator of epidermal innate immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(10):e1003660. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003660. Epub 2013 Oct 17. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24146615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrieu S, Gillette S, Amouyal K, Nourhashemi F, Reynish E, Ousset PJ, Albarede JL, Vellas B, Grandjean H. Association of Alzheimer's disease onset with Ginkgo biloba and other symptomatic cognitive treatments in a population of women aged 75 years and older from the EPIDOS study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003;58:372–377. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, Hartwieg E, Horvitz HR. Odorant-selective genes and neurons mediate olfaction in C. elegans . Cell. 1993;74:515–527. - PubMed
-
- Bastianetto S, Ramassamy C, Dore S, Christen Y, Poirier J, Quirion R. The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by beta-amyloid. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:1882–1890. - PubMed
-
- Birks J, Grimley EV, Van Dongen M. Ginkgo biloba for cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;4:CD003120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
