A verification protocol for the probe sequences of Affymetrix genome arrays reveals high probe accuracy for studies in mouse, human and rat
- PMID: 17448222
- PMCID: PMC1865557
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-132
A verification protocol for the probe sequences of Affymetrix genome arrays reveals high probe accuracy for studies in mouse, human and rat
Abstract
Background: The Affymetrix GeneChip technology uses multiple probes per gene to measure its expression level. Individual probe signals can vary widely, which hampers proper interpretation. This variation can be caused by probes that do not properly match their _target gene or that match multiple genes. To determine the accuracy of Affymetrix arrays, we developed an extensive verification protocol, for mouse arrays incorporating the NCBI RefSeq, NCBI UniGene Unique, NIA Mouse Gene Index, and UCSC mouse genome databases.
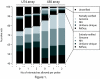
Results: Applying this protocol to Affymetrix Mouse Genome arrays (the earlier U74Av2 and the newer 430 2.0 array), the number of sequence-verified probes with perfect matches was no less than 85% and 95%, respectively; and for 74% and 85% of the probe sets all probes were sequence verified. The latter percentages increased to 80% and 94% after discarding one or two unverifiable probes per probe set, and even further to 84% and 97% when, in addition, allowing for one or two mismatches between probe and _target gene. Similar results were obtained for other mouse arrays, as well as for human and rat arrays. Based on these data, refined chip definition files for all arrays are provided online. Researchers can choose the version appropriate for their study to (re)analyze expression data.
Conclusion: The accuracy of Affymetrix probe sequences is higher than previously reported, particularly on newer arrays. Yet, refined probe set definitions have clear effects on the detection of differentially expressed genes. We demonstrate that the interpretation of the results of Affymetrix arrays is improved when the new chip definition files are used.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcript-level annotation of Affymetrix probesets improves the interpretation of gene expression data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Jun 11;8:194. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-194. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17559689 Free PMC article.
-
Splicy: a web-based tool for the prediction of possible alternative splicing events from Affymetrix probeset data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Mar 8;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-S1-S17. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17430561 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of probe coverage for high-resolution oligonucleotide aCGH.Bioinformatics. 2007 Jan 15;23(2):e77-83. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl316. Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17237109
-
Using oligonucleotide probe arrays to access genetic diversity.Biotechniques. 1995 Sep;19(3):442-7. Biotechniques. 1995. PMID: 7495558 Review.
-
Creation of the whole human genome microarray.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2004 Jun;1(1):19-28. doi: 10.1586/14789450.1.1.19. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2004. PMID: 15966795 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic architecture of gene expression in ovine skeletal muscle.BMC Genomics. 2011 Dec 15;12:607. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-607. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22171619 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of new mask protocols for gene expression profiling in humans and chimpanzees.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Mar 5;10:77. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-77. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19265541 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

