Modulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vivo regulates systemic iron balance
- PMID: 17607365
- PMCID: PMC1904317
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31342
Modulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vivo regulates systemic iron balance
Abstract
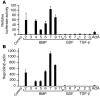
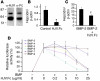
Systemic iron balance is regulated by hepcidin, a peptide hormone secreted by the liver. By decreasing cell surface expression of the iron exporter ferroportin, hepcidin decreases iron absorption from the intestine and iron release from reticuloendothelial stores. Hepcidin excess has been implicated in the pathogenesis of anemia of chronic disease, while hepcidin deficiency has a key role in the pathogenesis of the iron overload disorder hemochromatosis. We have recently shown that hemojuvelin is a coreceptor for bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling and that BMP signaling positively regulates hepcidin expression in liver cells in vitro. Here we show that BMP-2 administration increases hepcidin expression and decreases serum iron levels in vivo. We also show that soluble hemojuvelin (HJV.Fc) selectively inhibits BMP induction of hepcidin expression in vitro and that administration of HJV.Fc decreases hepcidin expression, increases ferroportin expression, mobilizes splenic iron stores, and increases serum iron levels in vivo. These data support a role for modulators of the BMP signaling pathway in treating diseases of iron overload and anemia of chronic disease.
Figures
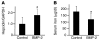
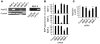
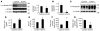
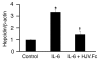
Comment in
-
Hepcidin regulation: ironing out the details.J Clin Invest. 2007 Jul;117(7):1755-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI32701. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17607352 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Hepcidin regulation: ironing out the details.J Clin Invest. 2007 Jul;117(7):1755-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI32701. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17607352 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein signaling by hemojuvelin regulates hepcidin expression.Nat Genet. 2006 May;38(5):531-9. doi: 10.1038/ng1777. Epub 2006 Apr 9. Nat Genet. 2006. PMID: 16604073
-
Hemojuvelin regulates hepcidin expression via a selective subset of BMP ligands and receptors independently of neogenin.Blood. 2008 May 15;111(10):5195-204. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-111567. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18326817 Free PMC article.
-
Update on iron metabolism and molecular perspective of common genetic and acquired disorder, hemochromatosis.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015 Jul;95(1):12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.02.006. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25737209 Review.
-
Modulation of hepcidin to treat iron deregulation: potential clinical applications.Expert Rev Hematol. 2016;9(2):169-86. doi: 10.1586/17474086.2016.1124757. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Expert Rev Hematol. 2016. PMID: 26669208 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular biology, genetics and biochemistry of the repulsive guidance molecule family.Biochem J. 2009 Aug 27;422(3):393-403. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090978. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19698085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neogenin inhibits HJV secretion and regulates BMP-induced hepcidin expression and iron homeostasis.Blood. 2010 Apr 15;115(15):3136-45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-251199. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20065295 Free PMC article.
-
Established and Emerging Concepts to Treat Imbalances of Iron Homeostasis in Inflammatory Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 Dec 11;11(4):135. doi: 10.3390/ph11040135. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30544952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble Hemojuvelin and Ferritin: Potential Prognostic Markers in Pediatric Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;15(4):1041. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041041. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831385 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia attenuates inflammation-induced hepcidin synthesis during experimental human endotoxemia.Haematologica. 2019 Jun;104(6):e230-e232. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.202796. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30655372 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Weiss G., Goodnough L.T. Anemia of chronic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;352:1011–1023. - PubMed
-
- Pigeon C., et al. A new mouse liver-specific gene, encoding a protein homologous to human antimicrobial peptide hepcidin, is overexpressed during iron overload. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:7811–7819. - PubMed
-
- Nemeth E., et al. Hepcidin, a putative mediator of anemia of inflammation, is a type II acute-phase protein. Blood. 2003;101:2461–2463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

