Accuracy and quality of massively parallel DNA pyrosequencing
- PMID: 17659080
- PMCID: PMC2323236
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-7-r143
Accuracy and quality of massively parallel DNA pyrosequencing
Abstract
Background: Massively parallel pyrosequencing systems have increased the efficiency of DNA sequencing, although the published per-base accuracy of a Roche GS20 is only 96%. In genome projects, highly redundant consensus assemblies can compensate for sequencing errors. In contrast, studies of microbial diversity that catalogue differences between PCR amplicons of ribosomal RNA genes (rDNA) or other conserved gene families cannot take advantage of consensus assemblies to detect and minimize incorrect base calls.
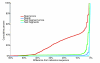
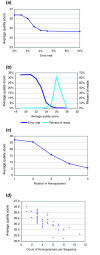
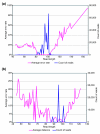
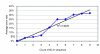
Results: We performed an empirical study of the per-base error rate for the Roche GS20 system using sequences of the V6 hypervariable region from cloned microbial ribosomal DNA (tag sequencing). We calculated a 99.5% accuracy rate in unassembled sequences, and identified several factors that can be used to remove a small percentage of low-quality reads, improving the accuracy to 99.75% or better.
Conclusion: By using objective criteria to eliminate low quality data, the quality of individual GS20 sequence reads in molecular ecological applications can surpass the accuracy of traditional capillary methods.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates.Environ Microbiol. 2010 Jan;12(1):118-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.02051.x. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19725865
-
Analysis of microbial diversity by pyrosequencing the small-subunit ribosomal RNA without PCR amplification.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Apr;98(8):3777-89. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5583-0. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24531274
-
Serial analysis of V6 ribosomal sequence tags (SARST-V6): a method for efficient, high-throughput analysis of microbial community composition.Environ Microbiol. 2005 Mar;7(3):356-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00712.x. Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15683396
-
Patterns of sequence variation in two regions of the 16S rRNA multigene family of Escherichia coli.Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999 Apr;49 Pt 2:601-10. doi: 10.1099/00207713-49-2-601. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10319482
-
Improving the quality of automatic DNA sequence assembly using fluorescent trace-data classifications.Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1996;4:3-14. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8877499 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Sequencing of the HIV-1 env Gene Reveals Discrete X4 Lineages and Linkage Disequilibrium between X4 and R5 Viruses in the V1/V2 and V3 Variable Regions.J Virol. 2016 Jul 27;90(16):7142-58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00441-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27226378 Free PMC article.
-
Fast skeletal muscle transcriptome of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) determined by next generation sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 11;13:181. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-181. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22577894 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges with using primer IDs to improve accuracy of next generation sequencing.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 5;10(3):e0119123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119123. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25741706 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic Insights into Effects of Chemical Pollutants on Microbial Community Composition and Function in Estuarine Sediments Receiving Polluted River Water.Microb Ecol. 2017 May;73(4):791-800. doi: 10.1007/s00248-016-0868-8. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Microb Ecol. 2017. PMID: 27744476
-
Phaeocystis antarctica blooms strongly influence bacterial community structures in the Amundsen Sea polynya.Front Microbiol. 2014 Dec 19;5:646. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00646. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25566197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldberg SMD, Johnson J, Busam D, Feldblyum T, Ferriera S, Friedman R, Halpern A, Khouri H, Kravitz SA, Lauro FM, et al. A Sanger/pyrosequencing hybrid approach for the generation of high-quality draft assemblies of marine microbial genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:11240–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604351103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

