Identification of IRS-1 Ser-1101 as a _target of S6K1 in nutrient- and obesity-induced insulin resistance
- PMID: 17709744
- PMCID: PMC1950339
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706517104
Identification of IRS-1 Ser-1101 as a _target of S6K1 in nutrient- and obesity-induced insulin resistance
Abstract
S6K1 has emerged as a critical signaling component in the development of insulin resistance through phosphorylation and inhibition of IRS-1 function. This effect can be triggered directly by nutrients such as amino acids or by insulin through a homeostatic negative-feedback loop. However, the role of S6K1 in mediating IRS-1 phosphorylation in a physiological setting of nutrient overload is unresolved. Here we show that S6K1 directly phosphorylates IRS-1 Ser-1101 in vitro in the C-terminal domain of the protein and that mutation of this site largely blocks the ability of amino acids to suppress IRS-1 tyrosine and Akt phosphorylation. Consistent with this finding, phosphorylation of IRS-1 Ser-1101 is increased in the liver of obese db/db and wild-type, but not S6K1(-/-), mice maintained on a high-fat diet and is blocked by siRNA knockdown of S6K1 protein. Finally, infusion of amino acids in humans leads to the concomitant activation of S6K1, phosphorylation of IRS-1 Ser-1101, a reduction in IRS-1 function, and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. These findings indicate that nutrient- and hormonal-dependent activation of S6K1 causes insulin resistance in mice and humans, in part, by mediating IRS-1 Ser-1101 phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
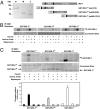
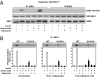
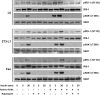
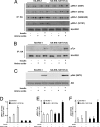
Similar articles
-
S6K directly phosphorylates IRS-1 on Ser-270 to promote insulin resistance in response to TNF-(alpha) signaling through IKK2.J Biol Chem. 2008 Dec 19;283(51):35375-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806480200. Epub 2008 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18952604 Free PMC article.
-
Serine phosphorylation proximal to its phosphotyrosine binding domain inhibits insulin receptor substrate 1 function and promotes insulin resistance.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(21):9668-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.21.9668-9681.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15485932 Free PMC article.
-
Increased activation of the mammalian _target of rapamycin pathway in liver and skeletal muscle of obese rats: possible involvement in obesity-linked insulin resistance.Endocrinology. 2005 Mar;146(3):1473-81. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0921. Epub 2004 Dec 16. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15604215
-
Ser/Thr phosphorylation of IRS proteins: a molecular basis for insulin resistance.Sci STKE. 2005 Jan 25;2005(268):pe4. doi: 10.1126/stke.2682005pe4. Sci STKE. 2005. PMID: 15671481 Review.
-
Nutrient overload, insulin resistance, and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1, S6K1.Cell Metab. 2006 Jun;3(6):393-402. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.003. Cell Metab. 2006. PMID: 16753575 Review.
Cited by
-
Sexual dimorphism in the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance during a critical developmental window in Wistar rats.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Oct 12;20(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00965-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36224569 Free PMC article.
-
ADP Induces Blood Glucose Through Direct and Indirect Mechanisms in Promotion of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis by Elevation of NADH.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 27;12:663530. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.663530. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33986729 Free PMC article.
-
Astaxanthin Inhibits p70 S6 Kinase 1 Activity to Sensitize Insulin Signaling.Mar Drugs. 2020 Sep 28;18(10):495. doi: 10.3390/md18100495. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32998286 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of H2O2 generated by NOX4 during cellular response under glucose deprivation.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e56628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056628. Epub 2013 Mar 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555559 Free PMC article.
-
Basal MET phosphorylation is an indicator of hepatocyte dysregulation in liver disease.Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Mar;20(3):187-216. doi: 10.1038/s44320-023-00007-4. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Mol Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 38216754 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

