Mutational analysis of steroidogenic factor 1 (NR5a1) in 24 boys with bilateral anorchia: a French collaborative study
- PMID: 17940071
- PMCID: PMC2990861
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dem278
Mutational analysis of steroidogenic factor 1 (NR5a1) in 24 boys with bilateral anorchia: a French collaborative study
Abstract
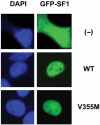
BACKGROUND Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1/AdBP4/FTZF1, NR5A1) is a nuclear receptor transcription factor that plays a key role in regulating adrenal and gonadal development, steroidogenesis and reproduction. Recently, haploinsufficiency of SF1 has been described in several 46,XY individuals with mild gonadal dysgenesis and impaired androgenization, but normal adrenal function, suggesting that dosage-sensitive or domain-specific effects of SF1 action are important in human testicular development and function. Our objective was to investigate whether partial defects in SF1 function might be associated with milder male reproductive phenotypes, such as bilateral anorchia ('vanishing testis syndrome') and micropenis. METHODS This study involved mutational analysis of NR5A1 in 24 individuals with bilateral anorchia and micropenis from the French Collaborative Anorchia study, as well as in vitro functional studies of SF1-dependent transcriptional activation and computer modeling. RESULTS A novel heterozygous missense mutation (V355M) in SF1 was found in one boy with a micropenis and testicular regression syndrome. This non-synonymous change was found to affect a highly conserved amino acid within helix 7 of the ligand-binding domain of SF1. This V355M mutation did not affect stability or nuclear localization, but did result in an approximately 50% reduction in SF1 activity in several different assay systems. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, heterozygous partial loss of function mutations in SF1 may be associated with bilateral anorchia ('vanishing testis syndrome') and micropenis in humans.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heterozygous missense mutations in steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1/Ad4BP, NR5A1) are associated with 46,XY disorders of sex development with normal adrenal function.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Mar;92(3):991-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1672. Epub 2007 Jan 2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17200175 Free PMC article.
-
Five novel mutations in steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1, NR5A1) in 46,XY patients with severe underandrogenization but without adrenal insufficiency.Hum Mutat. 2008 Jan;29(1):59-64. doi: 10.1002/humu.20588. Hum Mutat. 2008. PMID: 17694559 Free PMC article.
-
Update--steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1, NR5A1).Minerva Endocrinol. 2010 Jun;35(2):73-86. Minerva Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20595937 Review.
-
Analysis of the gene coding for steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1, NR5A1) in a cohort of 50 Egyptian patients with 46,XY disorders of sex development.Eur J Endocrinol. 2014 Apr 10;170(5):759-67. doi: 10.1530/EJE-13-0965. Print 2014 May. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24591553
-
Testicular dysgenesis without adrenal insufficiency in a 46,XY patient with a heterozygous inactive mutation of steroidogenic factor-1.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Dec;89(12):5930-5. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0935. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15579739 Review.
Cited by
-
A fish with no sex: gonadal and adrenal functions partition between zebrafish NR5A1 co-orthologs.Genetics. 2021 Feb 9;217(2):iyaa030. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyaa030. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33724412 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic characteristics of a large international cohort of individuals with rare NR5A1/SF-1 variants of sex development.EBioMedicine. 2024 Jan;99:104941. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104941. Epub 2024 Jan 1. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38168586 Free PMC article.
-
Steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, Ad4BP, NR5A1) and disorders of testis development.Sex Dev. 2008;2(4-5):200-9. doi: 10.1159/000152036. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Sex Dev. 2008. PMID: 18987494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent findings on the genetics of disorders of sex development.Curr Opin Urol. 2017 Jan;27(1):1-6. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000000353. Curr Opin Urol. 2017. PMID: 27798415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroidogenic factor-1 and human disease.Semin Reprod Med. 2012 Oct;30(5):374-81. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1324720. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Semin Reprod Med. 2012. PMID: 23044873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abeyaratne WA, Aherne WA, Scott JE. The vanishing testis. Lancet. 1969;2:822–841. - PubMed
-
- Achermann JC, Ito M, Ito M, Hindmarsh PC, Jameson JL. A mutation in the gene encoding steroidogenic factor-1 causes XY sex reversal and adrenal failure in humans. Nat Genet. 1999;22:125–126. - PubMed
-
- Achermann JC, Ito M, Silverman BL, Habiby RL, Pang S, Rosler A, Jameson JL. Missense mutations cluster within the carboxy-terminal region of DAX-1 and impair transcriptional repression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:3171–3175. - PubMed
-
- Achermann JC, Ozisik G, Ito M, Orun UA, Harmanci K, Gurakan B, Jameson JL. Gonadal determination and adrenal development are regulated by the orphan nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor-1, in a dose-dependent manner. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1829–1833. - PubMed
-
- Aynsley-Green A, Zachmann M, Illig R, Rampini S, Prader A. Congenital bilateral anorchia in childhood: a clinical, endocrine and therapeutic evaluation of twenty-one cases. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976;5:381–385. - PubMed

