Strongyloides stercoralis: cell- and tissue-specific transgene expression and co-transformation with vector constructs incorporating a common multifunctional 3' UTR
- PMID: 17945217
- PMCID: PMC2259275
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exppara.2007.08.018
Strongyloides stercoralis: cell- and tissue-specific transgene expression and co-transformation with vector constructs incorporating a common multifunctional 3' UTR
Abstract
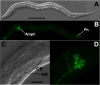
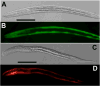
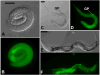
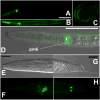
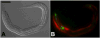
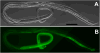
Transgenesis is a valuable methodology for studying gene expression patterns and gene function. It has recently become available for research on some parasitic nematodes, including Strongyloides stercoralis. Previously, we described a vector construct, comprising the promoter and 3' UTR of the S. stercoralis gene Ss era-1 that gives expression of GFP in intestinal cells of developing F1 progeny. In the present study, we identified three new S. stercoralis promoters, which, in combination with the Ss era-1 3' UTR, can drive expression of GFP or the red fluorescent protein, mRFPmars, in tissue-specific fashion. These include Ss act-2, which drives expression in body wall muscle cells, Ss gpa-3, which drives expression in amphidial and phasmidial neurons and Ss rps-21, which drives ubiquitous expression in F1 transformants and in the gonads of microinjected P0 female worms. Concomitant microinjection of vectors containing GFP and mRFPmars gave dually transformed F1 progeny, suggesting that these constructs could be used as co-injection markers for other transgenes of interest. We have developed a vector "toolkit" for S. stercoralis including constructs with the Ss era-1 3' UTR and each of the promoters described above.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful transgenesis of the parasitic nematode Strongyloides stercoralis requires endogenous non-coding control elements.Int J Parasitol. 2006 May 31;36(6):671-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.12.007. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Int J Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16500658
-
Heritable genetic transformation of Strongyloides stercoralis by microinjection of plasmid DNA constructs into the male germline.Int J Parasitol. 2017 Aug;47(9):511-515. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Int J Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28577882 Free PMC article.
-
Transgene expression in Strongyloides stercoralis following gonadal microinjection of DNA constructs.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002 Feb;119(2):279-84. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(01)00414-5. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002. PMID: 11814580 No abstract available.
-
Strongyloides stercoralis: a model for translational research on parasitic nematode biology.WormBook. 2007 Feb 17:1-18. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.134.1. WormBook. 2007. PMID: 18050500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenesis in Strongyloides and related parasitic nematodes: historical perspectives, current functional genomic applications and progress towards gene disruption and editing.Parasitology. 2017 Mar;144(3):327-342. doi: 10.1017/S0031182016000391. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Parasitology. 2017. PMID: 27000743 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Critical Role for Thermosensation in Host Seeking by Skin-Penetrating Nematodes.Curr Biol. 2018 Jul 23;28(14):2338-2347.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.05.063. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 30017486 Free PMC article.
-
Terror in the dirt: Sensory determinants of host seeking in soil-transmitted mammalian-parasitic nematodes.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018 Dec;8(3):496-510. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Oct 26. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 30396862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenic expression of a T cell epitope in Strongyloides ratti reveals that helminth-specific CD4+ T cells constitute both Th2 and Treg populations.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jul 8;17(7):e1009709. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009709. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34237106 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi mediated gene knockdown and transgenesis by microinjection in the necromenic Nematode Pristionchus pacificus.J Vis Exp. 2011 Oct 16;(56):e3270. doi: 10.3791/3270. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 22025167 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics of hsp-90 in parasitic and free-living nematodes.Int J Parasitol. 2009 Aug;39(10):1071-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.02.024. Epub 2009 May 3. Int J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19401205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashton FT, Bhopale VM, Fine AE, Schad GA. Sensory neuroanatomy of a skin-penetrating nematode parasite: Strongyloides stercoralis. I. Amphidial neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1995;357:281–95. - PubMed
-
- Ashton FT, Bhopale VM, Holt D, Smith G, Schad GA. Developmental switching in the parasitic nematode Strongyloides stercoralis is controlled by the ASF and ASI amphidial neurons. Journal of Parasitology. 1998;84:691–695. - PubMed
-
- Britton C, Redmond DL, Knox DP, McKerrow JH, Barry JD. Identification of promoter elements of parasite nematode genes in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology. 1999;103:171–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

