Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses
- PMID: 17974687
- PMCID: PMC2048840
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39343.408449.80
Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses
Abstract
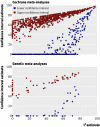
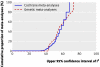
John Ioannidis, Nikolaos Patsopoulos, and Evangelos Evangelou argue that, although meta-analyses often measure heterogeneity between studies, these estimates can have large uncertainty, which must be taken into account when interpreting evidence
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity and statistical significance in meta-analysis: an empirical study of 125 meta-analyses.Stat Med. 2000 Jul 15;19(13):1707-28. doi: 10.1002/1097-0258(20000715)19:13<1707::aid-sim491>3.0.co;2-p. Stat Med. 2000. PMID: 10861773 Review.
-
Methods to calculate uncertainty in the estimated overall effect size from a random-effects meta-analysis.Res Synth Methods. 2019 Mar;10(1):23-43. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1319. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Res Synth Methods. 2019. PMID: 30129707
-
Incorporating uncertainty regarding applicability of evidence from meta-analyses into clinical decision making.J Clin Epidemiol. 2014 Mar;67(3):325-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Dec 12. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24332396
-
A Bayesian Power Analysis Procedure Considering Uncertainty in Effect Size Estimates from a Meta-analysis.Multivariate Behav Res. 2016 Sep-Oct;51(5):589-605. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2016.1191324. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Multivariate Behav Res. 2016. PMID: 27485763
-
Uncertainty method improved on best-worst case analysis in a binary meta-analysis.J Clin Epidemiol. 2005 Jun;58(6):579-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.09.013. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005. PMID: 15878471 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative assessment of the association between TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism and bladder cancer risk.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Mar;40(3):2389-95. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2319-z. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23184052
-
Prognostic Values of Vimentin Expression and Its Clinicopathological Significance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies with 4118 Cases.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 22;11(9):e0163162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163162. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27657690 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of low-carbohydrate diet on health status: an umbrella review.Front Nutr. 2024 Sep 25;11:1321198. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1321198. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39385794 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of the association between MTHFR C677T polymorphism and colorectal cancer risk in East Asians.Tumour Biol. 2012 Dec;33(6):2041-51. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0463-7. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Tumour Biol. 2012. PMID: 22890827
-
Recurrence-free survival after total thyroidectomy and lobectomy in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma.J Endocrinol Invest. 2021 Apr;44(4):725-734. doi: 10.1007/s40618-020-01342-1. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021. PMID: 32651895
References
-
- Lau J, Ioannidis JPA, Schmid CH. Summing up evidence: one answer is not always enough. Lancet 1998;351:123-7. - PubMed
-
- Sutton A, Abrams K, Jones D, Sheldon T, Song F. Methods for meta-analysis in medical research Chichester: Wiley, 2000
-
- Petitti DB. Approaches to heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat Med 2001;20:3625-33. - PubMed
-
- Cochran WG. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954;10:101-29.
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002;21:1539-58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
