Nuclear respiratory factor 1 regulates all ten nuclear-encoded subunits of cytochrome c oxidase in neurons
- PMID: 18077450
- PMCID: PMC2669777
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M707587200
Nuclear respiratory factor 1 regulates all ten nuclear-encoded subunits of cytochrome c oxidase in neurons
Abstract
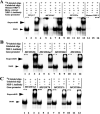
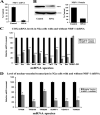
Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) is one of only four bigenomic proteins in mammalian cells, having ten subunits encoded in the nuclear genome and three in the mitochondrial DNA. The mechanism of its bigenomic control is not well understood. The ten nuclear subunits are on different chromosomes, and the possibility of their coordinate regulation by the same transcription factor(s) deserves serious consideration. The present study tested our hypothesis that nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF-1) serves such a role in subunit coordination. Following in silico analysis of murine nuclear-encoded COX subunit promoters, electrophoretic mobility shift and supershift assays indicated NRF-1 binding to all ten promoters. In vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation assays also showed NRF-1 binding to all ten promoters in murine neuroblastoma cells. Site-directed mutagenesis of putative NRF-1 binding sites confirmed the functionality of NRF-1 binding on all ten COX promoters. These sites are highly conserved among mice, rats, and humans. Silencing of NRF-1 with RNA interference reduced all ten COX subunit mRNAs and mRNAs of other genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. We conclude that NRF-1 plays a significant role in coordinating the transcriptional regulation of all ten nuclear-encoded COX subunits in neurons. Moreover, NRF-1 is known to activate mitochondrial transcription factors A and B, thereby indirectly regulating the expressions of the three mitochondrial-encoded COX subunits. Thus, NRF-1 and our previously described NRF-2 prove to be the two key bigenomic coordinators for transcriptional regulation of all cytochrome c oxidase subunits in neurons. Possible interactions between the NRFs will be investigated in the future.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bigenomic regulation of cytochrome c oxidase in neurons and the tight coupling between neuronal activity and energy metabolism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;748:283-304. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-3573-0_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22729863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is nuclear respiratory factor 2 a master transcriptional coordinator for all ten nuclear-encoded cytochrome c oxidase subunits in neurons?Gene. 2005 Oct 24;360(1):65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.015. Epub 2005 Aug 26. Gene. 2005. PMID: 16126350
-
Coupling of energy metabolism and synaptic transmission at the transcriptional level: role of nuclear respiratory factor 1 in regulating both cytochrome c oxidase and NMDA glutamate receptor subunit genes.J Neurosci. 2009 Jan 14;29(2):483-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3704-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19144849 Free PMC article.
-
Bigenomic transcriptional regulation of all thirteen cytochrome c oxidase subunit genes by specificity protein 1.Open Biol. 2013 Mar 20;3(3):120176. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120176. Open Biol. 2013. PMID: 23516108 Free PMC article.
-
Structural organization and transcription regulation of nuclear genes encoding the mammalian cytochrome c oxidase complex.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1998;61:309-44. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60830-2. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9752724 Review.
Cited by
-
Bigenomic regulation of cytochrome c oxidase in neurons and the tight coupling between neuronal activity and energy metabolism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;748:283-304. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-3573-0_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22729863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial function and oxidative stress in white adipose tissue in a rat model of PCOS: effect of SGLT2 inhibition.Biol Sex Differ. 2022 Aug 19;13(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13293-022-00455-x. Biol Sex Differ. 2022. PMID: 35986388 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of COX6c in the regulation of oxidative phosphorylation and diseases.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Jul 25;8(1):336. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01130-1. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35879322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac nuclear receptors: architects of mitochondrial structure and function.J Clin Invest. 2017 Apr 3;127(4):1155-1164. doi: 10.1172/JCI88888. Epub 2017 Feb 13. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28192373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhein Relieves Oxidative Stress in an Aβ1-42 Oligomer-Burdened Neuron Model by Activating the SIRT1/PGC-1α-Regulated Mitochondrial Biogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 10;12:746711. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.746711. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34566664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong-Riley MTT. Trends Neurosci. 1989;12:94–101. - PubMed
-
- Gunter TE, Gunter KK, Sheu SS, Gavin CE. Am. J. Physiol. 1994;267:C313–C339. - PubMed
-
- Manczak M, Anekonda TS, Henson E, Park BS, Quinn J, Reddy PH. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15:1437–1449. - PubMed
-
- Wong-Riley M, Antuono P, Ho KC, Egan R, Hevner R, Liebl W, Huang Z, Rachel R, Jones J. Vision Res. 1997;37:3593–3608. - PubMed
-
- Rahman S, Brown RM, Chong WK, Wilson CJ, Brown GK. Ann. Neurol. 2001;49:797–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

