The histone methyltransferase SET8 is required for S-phase progression
- PMID: 18166648
- PMCID: PMC2373509
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200706150
The histone methyltransferase SET8 is required for S-phase progression
Abstract
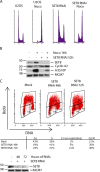
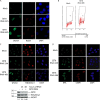
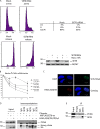
Chromatin structure and function is influenced by histone posttranslational modifications. SET8 (also known as PR-Set7 and SETD8) is a histone methyltransferase that monomethylates histonfe H4-K20. However, a function for SET8 in mammalian cell proliferation has not been determined. We show that small interfering RNA inhibition of SET8 expression leads to decreased cell proliferation and accumulation of cells in S phase. This is accompanied by DNA double-strand break (DSB) induction and recruitment of the DNA repair proteins replication protein A, Rad51, and 53BP1 to damaged regions. SET8 depletion causes DNA damage specifically during replication, which induces a Chk1-mediated S-phase checkpoint. Furthermore, we find that SET8 interacts with proliferating cell nuclear antigen through a conserved motif, and SET8 is required for DNA replication fork progression. Finally, codepletion of Rad51, an important homologous recombination repair protein, abrogates the DNA damage after SET8 depletion. Overall, we show that SET8 is essential for genomic stability in mammalian cells and that decreased expression of SET8 results in DNA damage and Chk1-dependent S-phase arrest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PR-Set7-dependent lysine methylation ensures genome replication and stability through S phase.J Cell Biol. 2007 Dec 31;179(7):1413-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200706179. Epub 2007 Dec 24. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 18158331 Free PMC article.
-
CRL4(Cdt2)-mediated destruction of the histone methyltransferase Set8 prevents premature chromatin compaction in S phase.Mol Cell. 2010 Oct 8;40(1):22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.015. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20932472 Free PMC article.
-
Direct interaction between SET8 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen couples H4-K20 methylation with DNA replication.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 25;283(17):11073-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700242200. Epub 2008 Mar 3. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18319261 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for the methyltransferase SETD8 in DNA damage repair.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Mar 4;14(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01251-5. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 35246238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the Development of Lysine Methyltransferase SETD8 Inhibitors.ChemMedChem. 2016 Aug 19;11(16):1680-5. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201600272. Epub 2016 Jul 14. ChemMedChem. 2016. PMID: 27411844 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of histone H4 lysine 20 methylation on 53BP1 responses to chromosomal double strand breaks.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049211. Epub 2012 Nov 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209566 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA inhibition in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Jul 1;88:123-37. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.12.006. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 25553957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting replicative stress to treat cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Jun;14(6):405-23. doi: 10.1038/nrd4553. Epub 2015 May 8. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 25953507 Review.
-
Inhibition of FBP1 expression by KMT5A through TWIST1 methylation is one of the mechanisms leading to chemoresistance in breast cancer.Oncol Rep. 2024 Aug;52(2):110. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8769. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38963044 Free PMC article.
-
Ageing-related chromatin defects through loss of the NURD complex.Nat Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;11(10):1261-7. doi: 10.1038/ncb1971. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Nat Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19734887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell, S.P., and A. Dutta. 2002. DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:333–374. - PubMed
-
- Fang, J., Q. Feng, C.S. Ketel, H. Wang, R. Cao, L. Xia, H. Erdjument-Bromage, P. Tempst, J.A. Simon, and Y. Zhang. 2002. Purification and functional characterization of SET8, a nucleosomal histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase. Curr. Biol. 12:1086–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

