Factor Xa stimulates proinflammatory and profibrotic responses in fibroblasts via protease-activated receptor-2 activation
- PMID: 18202198
- PMCID: PMC2312363
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070347
Factor Xa stimulates proinflammatory and profibrotic responses in fibroblasts via protease-activated receptor-2 activation
Abstract
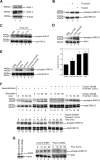
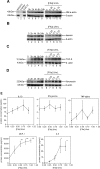
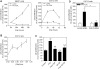
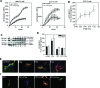
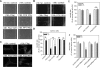
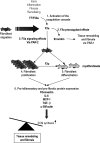
Coagulation proteases have been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of tissue remodeling and fibrosis. We therefore assessed the proinflammatory and fibroproliferative effects of coagulation protease factor (F)Xa. We show that FXa elicits a signaling response in C2C12 and NIH3T3 fibroblasts. FXa-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation was dependent on protease-activated receptor (PAR)-2 cleavage because desensitization with a PAR-2 agonist (trypsin) but not a PAR-1 agonist (thrombin) abolished FXa-induced signal transduction and PAR-2 siRNA abolished FXa-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. The PAR-2-dependent cellular effects of FXa led to fibroblast proliferation, migration, and differentiation into myofibroblasts, as demonstrated by the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and desmin, followed by the secretion of the cytokines monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and interleukin-6 as well as the expression of the fibrogenic proteins transforming growth factor-beta and fibronectin. To assess the relevance of FXa-induced proliferation and cell migration, we examined the effect of FXa in a wound scratch assay. Indeed, FXa facilitated wound healing in a PAR-2- and ERK1/2-dependent manner. Taken together, these results support the notion that, beyond its role in coagulation, FXa-dependent PAR-2 cleavage might play a role in the progression of tissue fibrosis and remodeling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is induced by thrombin and factor Xa in endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 2;279(14):13729-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400150200. Epub 2004 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14736878
-
Coagulation Factor Xa Induces Proinflammatory Responses in Cardiac Fibroblasts via Activation of Protease-Activated Receptor-1.Cells. 2021 Oct 30;10(11):2958. doi: 10.3390/cells10112958. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831181 Free PMC article.
-
Factor-Xa-induced mitogenesis and migration require sphingosine kinase activity and S1P formation in human vascular smooth muscle cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Aug 1;99(3):505-13. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt112. Epub 2013 May 7. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23658376
-
Blood coagulation factor Xa as an emerging drug _target.Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2011 Mar;15(3):341-9. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.553608. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2011. PMID: 21250873 Review.
-
Factor Xa: at the crossroads between coagulation and signaling in physiology and disease.Trends Mol Med. 2008 Oct;14(10):429-40. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Trends Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18774340 Review.
Cited by
-
Protease-activated receptor-2 induces myofibroblast differentiation and tissue factor up-regulation during bleomycin-induced lung injury: potential role in pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 2010 Dec;177(6):2753-64. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091107. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20971733 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinase-activated receptor-2 transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor and transforming growth factor-β receptor signaling pathways contributes to renal fibrosis.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37319-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.492793. Epub 2013 Nov 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24253040 Free PMC article.
-
Update on protease-activated receptor 2 in inflammatory and autoimmune dermatological diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 19;15:1449126. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1449126. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39364397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombin has biphasic effects on the nitric oxide-cGMP pathway in endothelial cells and contributes to experimental pulmonary hypertension.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 13;8(6):e63504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063504. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23785394 Free PMC article.
-
High endogenous activated protein C levels attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Nov;20(11):2029-2035. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12891. Epub 2016 Jun 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27295971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furie B, Furie BC. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988;53:505–518. - PubMed
-
- Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:349–363. - PubMed
-
- Darby I, Skalli O, Gabbiani G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed by myofibroblasts during experimental wound healing. Lab Invest. 1990;63:21–29. - PubMed
-
- Diegelmann RF, Evans MC. Wound healing: an overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front Biosci. 2004;9:283–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

