A mammalian microRNA cluster controls DNA methylation and telomere recombination via Rbl2-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferases
- PMID: 18311151
- PMCID: PMC2990406
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1399
A mammalian microRNA cluster controls DNA methylation and telomere recombination via Rbl2-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferases
Erratum in
- Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Sep;15(9):998
Abstract
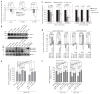
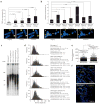
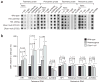
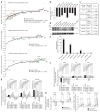
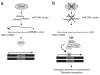
Dicer initiates RNA interference by generating small RNAs involved in various silencing pathways. Dicer participates in centromeric silencing, but its role in the epigenetic regulation of other chromatin domains has not been explored. Here we show that Dicer1 deficiency in Mus musculus leads to decreased DNA methylation, concomitant with increased telomere recombination and telomere elongation. These DNA-methylation defects correlate with decreased expression of Dnmt1, Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts), and methylation levels can be recovered by their overexpression. We identify the retinoblastoma-like 2 protein (Rbl2) as responsible for decreased Dnmt expression in Dicer1-null cells, suggesting the existence of Dicer-dependent small RNAs that _target Rbl2. We identify the miR-290 cluster as being downregulated in Dicer1-deficient cells and show that it silences Rbl2, thereby controlling Dnmt expression. These results identify a pathway by which miR-290 directly regulates Rbl2-dependent Dnmt expression, indirectly affecting telomere-length homeostasis.
Figures

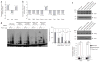

Similar articles
-
Normal DNA methylation dynamics in DICER1-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells.PLoS Genet. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002919. Epub 2012 Sep 6. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22969435 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs control de novo DNA methylation through regulation of transcriptional repressors in mouse embryonic stem cells.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Mar;15(3):259-67. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1391. Epub 2008 Mar 2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18311153
-
RBL2 bi-allelic truncating variants cause severe motor and cognitive impairment without evidence for abnormalities in DNA methylation or telomeric function.J Hum Genet. 2021 Nov;66(11):1101-1112. doi: 10.1038/s10038-021-00931-z. Epub 2021 May 13. J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33980986
-
The Roles of Human DNA Methyltransferases and Their Isoforms in Shaping the Epigenome.Genes (Basel). 2019 Feb 23;10(2):172. doi: 10.3390/genes10020172. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30813436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian DNA methyltransferases: new discoveries and open questions.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Oct 19;46(5):1191-1202. doi: 10.1042/BST20170574. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 30154093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-370 and miR-373 regulate the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by modulating one-carbon metabolism via SHMT-2 and MECP-2, respectively.Aging Cell. 2015 Oct;14(5):826-37. doi: 10.1111/acel.12363. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Aging Cell. 2015. PMID: 26103880 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review.EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Mar;4(3):143-59. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100209. Epub 2012 Feb 20. EMBO Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22351564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNAs regulate human embryonic stem cell division.Cell Cycle. 2009 Nov 15;8(22):3729-41. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.22.10033. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19823043 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and epigenetic regulation in the mammalian inner ear: implications for deafness.Mamm Genome. 2009 Sep-Oct;20(9-10):581-603. doi: 10.1007/s00335-009-9230-5. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Mamm Genome. 2009. PMID: 19876605 Review.
-
Maternal obesity and fetal metabolic programming: a fertile epigenetic soil.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):R711-22. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00310.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 14. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20631295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fukagawa T, et al. Dicer is essential for formation of the heterochromatin structure in vertebrate cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:784–791. - PubMed
-
- Volpe TA, et al. Regulation of heterochromatic silencing and histone H3 lysine-9 methylation by RNAi. Science. 2002;297:1833–1837. - PubMed
-
- Hall IM, et al. Establishment and maintenance of a heterochromatin domain. Science. 2002;297:2232–2237. - PubMed
-
- Pal-Bhadra M, et al. Heterochromatic silencing and HP1 localization in Drosophila are dependent on the RNAi machinery. Science. 2004;303:669–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

