Low-dose spironolactone reduces reactive oxygen species generation and improves insulin-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle in the TG(mRen2)27 rat
- PMID: 18445755
- PMCID: PMC2493595
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00258.2007
Low-dose spironolactone reduces reactive oxygen species generation and improves insulin-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle in the TG(mRen2)27 rat
Abstract
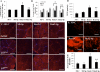
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) activation mediates increases in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and impaired insulin signaling. The transgenic Ren2 rat manifests increased tissue renin-angiotensin system activity, elevated serum aldosterone, hypertension, and insulin resistance. To explore the role of aldosterone in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance, we investigated the impact of in vivo treatment with a mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist on insulin sensitivity in Ren2 and aged-matched Sprague-Dawley (SD) control rats. Both groups (age 6-8 wk) were implanted with subcutaneous time-release pellets containing spironolactone (0.24 mg/day) or placebo over 21 days. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test were determined. Soleus muscle insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), tyrosine phosphorylated IRS-1, protein kinase B (Akt) phosphorylation, GLUT4 levels, and insulin-stimulated 2-deoxyglucose uptake were evaluated in relation to NADPH subunit expression/oxidase activity and ROS production (chemiluminescence and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal immunostaining). Along with increased soleus muscle NADPH oxidase activity and ROS, there was systemic insulin resistance and reduced muscle IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation, Akt phosphorylation/activation, and GLUT4 expression in the Ren2 group (each P < 0.05). Despite not decreasing blood pressure, low-dose spironolactone treatment improved soleus muscle insulin signaling parameters and systemic insulin sensitivity in concert with reductions in NADPH oxidase subunit expression/activity and ROS production (each P < 0.05). Our findings suggest that aldosterone contributes to insulin resistance in the transgenic Ren2, in part, by increasing NADPH oxidase activity in skeletal muscle tissue.
Figures
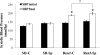
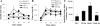
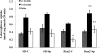
Similar articles
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism attenuates glomerular filtration barrier remodeling in the transgenic Ren2 rat.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 May;296(5):F1013-22. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90646.2008. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19261739 Free PMC article.
-
Direct renin inhibition improves systemic insulin resistance and skeletal muscle glucose transport in a transgenic rodent model of tissue renin overexpression.Endocrinology. 2009 Jun;150(6):2561-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1391. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19246535 Free PMC article.
-
Nebivolol improves insulin sensitivity in the TGR(Ren2)27 rat.Metabolism. 2011 Dec;60(12):1757-66. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.04.009. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Metabolism. 2011. PMID: 21640361 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of insulin sensitivity by antagonism of the renin-angiotensin system.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Sep;293(3):R974-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00147.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17581838 Review.
-
Role of oxidative stress in impaired insulin signaling associated with exercise-induced muscle damage.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:1265-1272. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.09.014. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 24075894 Review.
Cited by
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade attenuates hyperandrogenic metabolic dysregulation in letrozole-induced PCOS rat model.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Jul 15;21(2):1539-1547. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01097-x. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 36404823 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone decreases glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in vivo in mice and in murine islets.Diabetologia. 2011 Aug;54(8):2152-63. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2158-9. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21519965 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Salt and Glucose Intake on Angiotensin II and Aldosterone in Obese and Nonobese Patients with Essential Hypertension.Int J Hypertens. 2020 Mar 19;2020:6017105. doi: 10.1155/2020/6017105. eCollection 2020. Int J Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32257423 Free PMC article.
-
The renin angiotensin aldosterone system in hypertension: roles of insulin resistance and oxidative stress.Med Clin North Am. 2009 May;93(3):569-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2009.02.014. Med Clin North Am. 2009. PMID: 19427492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrastructure Study of Transgenic Ren2 Rat Aorta - Part 1: Endothelium and Intima.Cardiorenal Med. 2012 Feb;2(1):66-82. doi: 10.1159/000335565. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Cardiorenal Med. 2012. PMID: 22493605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdallah JG, Schrier RW, Edelstein C, Jennings SD, Wyse B, Ellison DH. Loop diuretic infusion increases thiazide-sensitive Na+/Cl−-cotransporter abundance: role of aldosterone. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 1335–1341, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Abo A, Pick A, Totty N, Teahan CG, Segal AW. Activation of the NADPH oxides involves the small GTP binding protein p21rac1. Nature 353: 668–670, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J Biol Chem 275: 9047–9054, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Blanco-Rivero J, Cachofeiro V, Lahera V, Aras-Lopez R, Marquez-Rodas I, Salaices M, Xavier FE, Ferrer M, Balfagon G. Participation of prostacyclin in endothelial dysfunction induced by aldosterone in normotensive hypertensive rats. Hypertension 46: 107–112, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Blendea MC, Jacobs D, Stump CS, McFarlane SI, Ogrin C, Bahtyiar G, Stas S, Kumar P, Sha Q, Ferrario CM, Sowers JR. Abrogation of oxidative stress improves insulin sensitivity in the Ren-2 rat model of tissue angiotensin II overexpression. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288: E353–E359, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

