Evolution of the mammalian transcription factor binding repertoire via transposable elements
- PMID: 18682548
- PMCID: PMC2577865
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.080663.108
Evolution of the mammalian transcription factor binding repertoire via transposable elements
Abstract
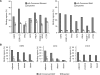
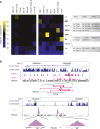
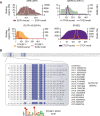
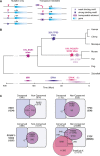
Identification of lineage-specific innovations in genomic control elements is critical for understanding transcriptional regulatory networks and phenotypic heterogeneity. We analyzed, from an evolutionary perspective, the binding regions of seven mammalian transcription factors (ESR1, TP53, MYC, RELA, POU5F1, SOX2, and CTCF) identified on a genome-wide scale by different chromatin immunoprecipitation approaches and found that only a minority of sites appear to be conserved at the sequence level. Instead, we uncovered a pervasive association with genomic repeats by showing that a large fraction of the bona fide binding sites for five of the seven transcription factors (ESR1, TP53, POU5F1, SOX2, and CTCF) are embedded in distinctive families of transposable elements. Using the age of the repeats, we established that these repeat-associated binding sites (RABS) have been associated with significant regulatory expansions throughout the mammalian phylogeny. We validated the functional significance of these RABS by showing that they are over-represented in proximity of regulated genes and that the binding motifs within these repeats have undergone evolutionary selection. Our results demonstrate that transcriptional regulatory networks are highly dynamic in eukaryotic genomes and that transposable elements play an important role in expanding the repertoire of binding sites.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolutionary rates and patterns for human transcription factor binding sites derived from repetitive DNA.BMC Genomics. 2008 May 17;9:226. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-226. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18485226 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable Elements and DNA Methylation Create in Embryonic Stem Cells Human-Specific Regulatory Sequences Associated with Distal Enhancers and Noncoding RNAs.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 May 7;7(6):1432-54. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv081. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25956794 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Rewiring of Human Regulatory Networks by Waves of Genome Expansion.Am J Hum Genet. 2018 Feb 1;102(2):207-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.12.014. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Am J Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29357977 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive sequences in complex genomes: structure and evolution.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007;8:241-59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.8.080706.092416. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17506661 Review.
-
TFs for TEs: the transcription factor repertoire of mammalian transposable elements.Genes Dev. 2021 Jan 1;35(1-2):22-39. doi: 10.1101/gad.344473.120. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 33397727 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hidden magicians of genome evolution.Indian J Med Res. 2013 Jun;137(6):1052-60. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23852286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placental Hypomethylation Is More Pronounced in Genomic Loci Devoid of Retroelements.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Jul 7;6(7):1911-21. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.030379. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27172225 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type differential _targeting of SETDB1 prevents aberrant CTCF binding, chromatin looping, and cis-regulatory interactions.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44578-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38167730 Free PMC article.
-
Primate-specific transposable elements shape transcriptional networks during human development.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 23;13(1):7178. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34800-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36418324 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary innovation in conserved regulatory elements across the mammalian tree of life.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 31:2024.01.31.578197. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.31.578197. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Oct 4;41(10):msae199. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae199 PMID: 38352419 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Barski A., Cuddapah S., Cui K., Roh T.Y., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Bejerano G., Lowe C.B., Ahituv N., King B., Siepel A., Salama S.R., Rubin E.M., Kent W.J., Haussler D. A distal enhancer and an ultraconserved exon are derived from a novel retroposon. Nature. 2006;441:87–90. - PubMed
-
- Bell A.C., West A.G., Felsenfeld G. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell. 1999;98:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Boffelli D., Nobrega M.A., Rubin E.M. Comparative genomics at the vertebrate extremes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004;5:456–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
