Differential effects of neonatal norepinephrine lesions on immediate early gene expression in developing and adult rat brain
- PMID: 18938224
- PMCID: PMC2657358
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.036
Differential effects of neonatal norepinephrine lesions on immediate early gene expression in developing and adult rat brain
Abstract
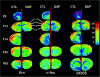
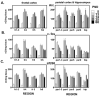
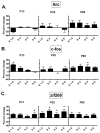
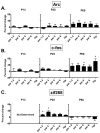
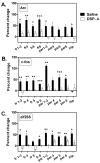
Activity regulated cytoskeletal protein (Arc), c-fos and zif268 are immediate early genes (IEGs) important for adult brain plasticity. We examined developmental expression of these IEGs and the effect of neonatal noradrenergic lesion on their expression in developing and mature brain. N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine hydrochloride (DSP-4), a specific noradrenergic neurotoxin, was administered to rats on postnatal day (PND) 3 and in situ hybridization was used to assay Arc, c-fos and zif268 mRNA on PND 13, 25 and 60. In contrast to decreases in Arc, c-fos and zif268 expression produced by noradrenergic lesions of mature brain, lesions on PND 3 yield a strikingly different effect. Neonatal lesions produce increases in c-fos and zif268 expression in specific frontal cortical layers on PND 13, while Arc shows no change. These lesions lead to increases in zif268 expression in frontal cortical layers on PND 25, with no changes in c-fos or Arc expression, and on PND 60 they produce a significant increase in c-fos expression in hippocampus with no significant changes in Arc or zif268 expression. 2-[2-(2-Methoxy-1,4-benzodioxanyl)]imidazoline hydrochloride (RX821002), an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor (A2AR) antagonist, administered to control PND 60 animals produces elevations of Arc, zif268 and c-fos mRNAs. This response was eliminated in animals lesioned with DSP-4 on PND 3. These data indicate that norepinephrine regulation of IEG expression differs in developing and mature brain and that loss of developmental norepinephrine leads to abnormally high postnatal IEG expression. Previous studies have shown an important role for norepinephrine in brain development. Our data support the idea that norepinephrine plays an important role during CNS development and that changes in noradrenergic signaling during development may have long lasting effects, potentially on learning and memory.
Figures
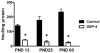
Similar articles
-
Changes in postnatal norepinephrine alter alpha-2 adrenergic receptor development.Neuroscience. 2011 Sep 29;192:761-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.045. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21742019 Free PMC article.
-
Experience-dependent gene expression in the rat hippocampus after spatial learning: a comparison of the immediate-early genes Arc, c-fos, and zif268.J Neurosci. 2001 Jul 15;21(14):5089-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-14-05089.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11438584 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of immediate early genes by nicotine after chronic neonatal nicotine exposure in brain areas involved in stress and anxiety responses.Brain Res. 2018 May 15;1687:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.027. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29496477
-
Selective Lifelong Destruction of Brain Monoaminergic Nerves Through Perinatal DSP-4 Treatment.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2016;29:51-71. doi: 10.1007/7854_2015_398. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26427851 Review.
-
Role of monoamine systems in activation of zif268 by cocaine.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1992 Sep;17(3):94-102. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1992. PMID: 1356432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of being Nernst: Synaptic activity and functional relevance in stem cell-derived neurons.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Jul 26;7(6):899-921. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.899. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 26240679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine is Required for Activity-Dependent Amplification of Arc mRNA in Developing Postnatal Frontal Cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2017 Jul 1;27(7):3600-3608. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhw181. Cereb Cortex. 2017. PMID: 27365296 Free PMC article.
-
Memory-enhancing corticosterone treatment increases amygdala norepinephrine and Arc protein expression in hippocampal synaptic fractions.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010 Mar;93(3):312-21. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2009.11.005. Epub 2009 Nov 22. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010. PMID: 19932757 Free PMC article.
-
Food for song: expression of c-Fos and ZENK in the zebra finch song nuclei during food aversion learning.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021157. Epub 2011 Jun 10. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695176 Free PMC article.
-
Interdependent adrenergic receptor regulation of Arc and Zif268 mRNA in cerebral cortex.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Jan 26;612:38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.12.002. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26655475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Berger-Sweeney J, Hohmann CF. Behavioral consequences of abnormal cortical development: insights into developmental disabilities. Behav Brain Res. 1997;86:121–142. - PubMed
-
- Blue ME, Parnavelas JG. The effect of neonatal 6-hydroxydopamine treatment on synaptogenesis in the visual cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1982;205:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Cirelli C, Pompeiano M, Tononi G. Neuronal gene expression in the waking state: a role for the locus coeruleus. Science. 1996;274:1211–1215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

