PTEN deficiency accelerates tumour progression in a mouse model of thyroid cancer
- PMID: 18997818
- PMCID: PMC3457778
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2008.407
PTEN deficiency accelerates tumour progression in a mouse model of thyroid cancer
Abstract
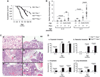
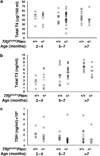
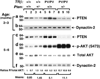
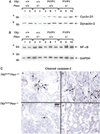
Inactivation and silencing of PTEN have been observed in multiple cancers, including follicular thyroid carcinoma. PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted from chromosome 10) functions as a tumour suppressor by opposing the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signalling pathway. Despite correlative data, how deregulated PTEN signalling leads to thyroid carcinogenesis is not known. Mice harbouring a dominant-negative mutant thyroid hormone receptor beta (TRbeta(PV/PV) mice) spontaneously develop follicular thyroid carcinoma and distant metastases similar to human cancer. To elucidate the role of PTEN in thyroid carcinogenesis, we generated TRbeta(PV/PV) mice haploinsufficient for Pten (TRbeta(PV/PV)Pten(+/-) mouse). PTEN deficiency accelerated the progression of thyroid tumour and increased the occurrence of metastasis spread to the lung in TRbeta(PV/PV)Pten(+/-) mice, thereby significantly reducing their survival as compared with TRbeta(PV/PV)Pten(+/+) mice. AKT activation was further increased by two-fold in TRbeta(PV/PV)Pten(+/-) mice thyroids, leading to increased activity of the downstream mammalian _target of rapamycin (mTOR)-p70S6K signalling and decreased activity of the forkhead family member FOXO3a. Consistently, cyclin D1 expression was increased. Apoptosis was decreased as indicated by increased expression of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and decreased caspase-3 activity in the thyroids of TRbeta(PV/PV)Pten(+/-) mice. Our results indicate that PTEN deficiency resulted in increased cell proliferation and survival in the thyroids of TRbeta(PV/PV)Pten(+/-) mice. Altogether, our study provides direct evidence to indicate that in vivo, PTEN is a critical regulator in the follicular thyroid cancer progression and invasiveness.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PI3K/AKT Pathway and Its Mediators in Thyroid Carcinomas.Mol Diagn Ther. 2016 Feb;20(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0175-y. Mol Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 26597586 Review.
-
Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delays tumor progression and blocks metastatic spread in a mouse model of thyroid cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2007 Dec;28(12):2451-8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm174. Epub 2007 Jul 28. Carcinogenesis. 2007. PMID: 17660507
-
AKT activation promotes metastasis in a mouse model of follicular thyroid carcinoma.Endocrinology. 2005 Oct;146(10):4456-63. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0172. Epub 2005 Jul 7. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 16002527
-
Inhibition of mTORC1 signaling reduces tumor growth but does not prevent cancer progression in a mouse model of thyroid cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Jul;31(7):1284-91. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq059. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20299527 Free PMC article.
-
Nongenomic activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling by thyroid hormone receptors.Steroids. 2009 Jul;74(7):628-34. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2008.10.009. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Steroids. 2009. PMID: 19014961 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Mar;13(3):184-99. doi: 10.1038/nrc3431. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23429735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin blocks progression of obesity-activated thyroid cancer in a mouse model.Onco_target. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):34832-44. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.8989. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27145454 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT Pathway and Its Mediators in Thyroid Carcinomas.Mol Diagn Ther. 2016 Feb;20(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0175-y. Mol Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 26597586 Review.
-
Fibrotic microenvironment promotes the metastatic seeding of tumor cells via activating the fibronectin 1/secreted phosphoprotein 1-integrin signaling.Onco_target. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):45702-45714. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.10157. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27329720 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte recruitment and activated inflammation are associated with thyroid carcinogenesis in a mouse model.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 1;9(7):1439-1453. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31392080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Latif MM, Kelleher D, Reynolds JV. Potential role of NF-kappaB in esophageal adenocarcinoma: as an emerging molecular _target. J Surg Res. 2008 (in press). - PubMed
-
- Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF, Carnero A. PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:1379–1386. - PubMed
-
- Di Cristofano A, Pesce B, Cordon-Cardo C, Pandolfi PP. Pten is essential for embryonic development and tumour suppression. Nat Genet. 1998;19:348–355. - PubMed
-
- Eng C. Role of PTEN, a lipid phosphatase upstream effector of protein kinase B, in epithelial thyroid carcinogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;968:213–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

