Bidirectional crosstalk between leptin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling promotes invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 19047149
- PMCID: PMC3180854
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1952
Bidirectional crosstalk between leptin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling promotes invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
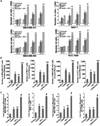
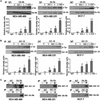
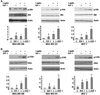
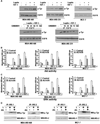
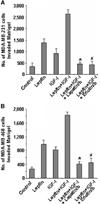
Obesity is an independent risk factor for breast cancer, and obese breast cancer patients exhibit a higher risk for larger tumor burden and increased metastasis. Obesity, as associated with metabolic syndrome, results in an increase in circulating insulin-like growth factor (IGF), which acts as a mitogen. In addition, higher plasma level of adipocytokine leptin is associated with obesity. In the present study, we show that cotreatment with leptin and IGF-I significantly increases proliferation as well as invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. We found a novel bidirectional crosstalk between leptin and IGF-I signaling; IGF-I induced phosphorylation of leptin receptor (Ob-Rb) and leptin induced phosphorylation of IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR), whereas cotreatment induced synergistic phosphorylation and association of Ob-Rb and IGF-IR along with activation of downstream effectors, Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Leptin increased phosphorylation of IGF signaling molecules insulin-receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2. Interestingly, we found that leptin and IGF-I cotreatment synergistically transactivated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), depending on the proteolytic release of EGFR ligands, as the broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor GM6001 could inhibit this effect. Using clinically relevant EGFR inhibitors, erlotinib and lapatinib, we found that inhibition of EGFR activation effectively inhibited leptin- and IGF-I-induced invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. Taken together, these data suggest a novel bidirectional crosstalk between leptin and IGF-I signaling that transactivates EGFR and promotes the metastatic properties as well as invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. Our findings indicate the possibility of using EGFR inhibitors erlotinib and lapatinib to counter the procancerous effects of leptin and IGF-I in breast cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel unidirectional cross-talk from the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor to leptin receptor in human breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Jun;6(6):1052-8. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2126. Epub 2008 May 30. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18515755 Free PMC article.
-
Transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor is involved in leptin-induced activation of janus-activated kinase 2 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in human gastric cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 15;65(20):9159-63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0598. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16230373
-
Lapatinib induces apoptosis in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cells: effects on insulin-like growth factor I signaling.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Feb;6(2):667-74. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0423. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17308062
-
Crosstalk between epidermal growth factor receptor- and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling: implications for cancer therapy.Curr Cancer Drug _targets. 2009 Sep;9(6):748-60. doi: 10.2174/156800909789271495. Curr Cancer Drug _targets. 2009. PMID: 19754359 Review.
-
Role of estrogen receptor alpha in modulating IGF-I receptor signaling and function in breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Sep;23(3):385-94. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15595626 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of HGF in obesity-associated tumorigenesis: C3(1)-TAg mice as a model for human basal-like breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Dec;142(3):489-503. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2741-5. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 24218051 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of leptin, leptin receptor, adiponectin, and adiponectin receptor in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive breast cancer.J Breast Cancer. 2011 Jun;14(2):96-103. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.2.96. Epub 2011 Jun 18. J Breast Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21847403 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing molecular mechanisms by integrating high-dimensional functional screens with protein interaction data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Sep 4;10(9):e1003801. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003801. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25188415 Free PMC article.
-
The tetrad BMI, leptin, leptin/adiponectin (L/A) ratio and CA 15-3 are reliable biomarkers of breast cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2013 Jan;27(1):12-20. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21555. Epub 2013 Jan 4. J Clin Lab Anal. 2013. PMID: 23292756 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol activates AMP-activated protein kinase in breast cancer cells via an LKB1-dependent pathway and inhibits breast carcinogenesis.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 21;14(1):R35. doi: 10.1186/bcr3128. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22353783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Newell B, Proust K, Dyball R, McManus P. Seeing obesity as a systems problem. N SW Public Health Bull. 2007;18:214–218. - PubMed
-
- Irigaray P, Newby JA, Lacomme S, Belpomme D. Overweight/obesity and cancer genesis: more than a biological link. Biomed Pharmacother. 2007;61:665–678. - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1625–1638. - PubMed
-
- Berclaz G, Li S, Price KN, et al. Body mass index as a prognostic feature in operable breast cancer: the International Breast Cancer Study Group experience. Ann Oncol. 2004;15:875–884. - PubMed
-
- Grodin JM, Siiteri PK, MacDonald PC. Source of estrogen production in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973;36:207–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01DK075397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA131294/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK071594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK089130/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK076742/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK061941/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062092/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK061941/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK077137/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK064399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK076742/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK064399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK062092/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

