H3K27me3 forms BLOCs over silent genes and intergenic regions and specifies a histone banding pattern on a mouse autosomal chromosome
- PMID: 19047520
- PMCID: PMC2652204
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.080861.108
H3K27me3 forms BLOCs over silent genes and intergenic regions and specifies a histone banding pattern on a mouse autosomal chromosome
Abstract
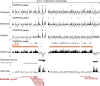
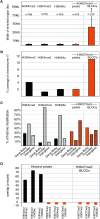
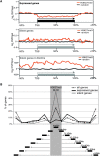
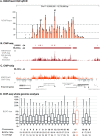
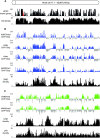
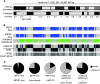
In mammals, genome-wide chromatin maps and immunofluorescence studies show that broad domains of repressive histone modifications are present on pericentromeric and telomeric repeats and on the inactive X chromosome. However, only a few autosomal loci such as silent Hox gene clusters have been shown to lie in broad domains of repressive histone modifications. Here we present a ChIP-chip analysis of the repressive H3K27me3 histone modification along chr 17 in mouse embryonic fibroblast cells using an algorithm named broad local enrichments (BLOCs), which allows the identification of broad regions of histone modifications. Our results, confirmed by BLOC analysis of a whole genome ChIP-seq data set, show that the majority of H3K27me3 modifications form BLOCs rather than focal peaks. H3K27me3 BLOCs modify silent genes of all types, plus flanking intergenic regions and their distribution indicates a negative correlation between H3K27me3 and transcription. However, we also found that some nontranscribed gene-poor regions lack H3K27me3. We therefore performed a low-resolution analysis of whole mouse chr 17, which revealed that H3K27me3 is enriched in mega-base-pair-sized domains that are also enriched for genes, short interspersed elements (SINEs) and active histone modifications. These genic H3K27me3 domains alternate with similar-sized gene-poor domains. These are deficient in active histone modifications, as well as H3K27me3, but are enriched for long interspersed elements (LINEs) and long-terminal repeat (LTR) transposons and H3K9me3 and H4K20me3. Thus, an autosome can be seen to contain alternating chromatin bands that predominantly separate genes from one retrotransposon class, which could offer unique domains for the specific regulation of genes or the silencing of autonomous retrotransposons.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histone chaperone CAF-1 mediates repressive histone modifications to protect preimplantation mouse embryos from endogenous retrotransposons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Nov 24;112(47):14641-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512775112. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26546670 Free PMC article.
-
H4K20me3 co-localizes with activating histone modifications at transcriptionally dynamic regions in embryonic stem cells.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jul 3;19(1):514. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4886-4. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29969988 Free PMC article.
-
Active and repressive chromatin are interspersed without spreading in an imprinted gene cluster in the mammalian genome.Mol Cell. 2007 Aug 3;27(3):353-66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.024. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17679087 Free PMC article.
-
The many faces of histone lysine methylation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;14(3):286-98. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(02)00335-6. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12067650 Review.
-
Broad Chromatin Domains: An Important Facet of Genome Regulation.Bioessays. 2017 Dec;39(12). doi: 10.1002/bies.201700124. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Bioessays. 2017. PMID: 29058338 Review.
Cited by
-
PRC2 inhibition counteracts the culture-associated loss of engraftment potential of human cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 22;5:12319. doi: 10.1038/srep12319. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26198814 Free PMC article.
-
Histone lysine methylation dynamics: establishment, regulation, and biological impact.Mol Cell. 2012 Nov 30;48(4):491-507. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.006. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 23200123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A KAP1 phosphorylation switch controls MyoD function during skeletal muscle differentiation.Genes Dev. 2015 Mar 1;29(5):513-25. doi: 10.1101/gad.254532.114. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25737281 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the DNA methyltransferase MET1 Induces H3K9 hypermethylation at PcG _target genes and redistribution of H3K27 trimethylation to transposons in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1003062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003062. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23209430 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin and epigenetic features of long-range gene regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(15):7185-99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt499. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23766291 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azuara V., Perry P., Sauer S., Spivakov M., Jorgensen H.F., John R.M., Gouti M., Casanova M., Warnes G., Merkenschlager M., et al. Chromatin signatures of pluripotent cell lines. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006;8:532–538. - PubMed
-
- Barski A., Cuddapah S., Cui K., Roh T.Y., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein B.E., Mikkelsen T.S., Xie X., Kamal M., Huebert D.J., Cuff J., Fry B., Meissner A., Wernig M., Plath K., et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006a;125:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
