Potential core species and satellite species in the bacterial community within the rabbit caecum
- PMID: 19049656
- PMCID: PMC2667309
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00611.x
Potential core species and satellite species in the bacterial community within the rabbit caecum
Abstract
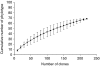
A bacteria library was constructed from the caecum of a rabbit maintained under standard conditions. The complete gene 16S rRNA gene was sequenced. The 228 clones obtained were distributed in 70 operational taxonomic units (OTUs). The large majority of the OTUs were composed of one or two clones and seven OTUs contained half of the sequences. Fourteen sequences had high similarity to the sequence already registered in databases (threshold of 97%). Only one of these sequences has been identified as Variovorax sp. (99% identity). Units were distributed mainly (94%) in the Firmicutes phylum. Three sequences were related to Bacteroidetes. Nine clusters were defined in the phylogenic tree. A great diversity of caecal bacteria of the rabbit was shown. Half of the sequences generated in this library were distributed in the phylogenetic tree near the sequences characterized previously in rabbit caecum (potential core species), and the other half of the sequences were well separated (satellite species).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular profiling of bacterial species in the rabbit caecum.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005 Mar 1;244(1):111-5. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.01.028. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15727829
-
Microbial diversity in ostrich ceca as revealed by 16S ribosomal RNA gene clone library and detection of novel Fibrobacter species.Anaerobe. 2010 Apr;16(2):83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2009.07.005. Epub 2009 Jul 24. Anaerobe. 2010. PMID: 19632349
-
Bacterial diversity in the rumen of Indian Surti buffalo (Bubalus bubalis), assessed by 16S rDNA analysis.J Appl Genet. 2010;51(3):395-402. doi: 10.1007/BF03208869. J Appl Genet. 2010. PMID: 20720314
-
First report on the bacterial diversity in the distal gut of dholes (Cuon alpinus) by using 16S rRNA gene sequences analysis.J Appl Genet. 2016 May;57(2):275-83. doi: 10.1007/s13353-015-0319-0. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 26423781
-
Novel and unexpected prokaryotic diversity in water and sediments of the alkaline, hypersaline lakes of the Wadi An Natrun, Egypt.Microb Ecol. 2007 Nov;54(4):598-617. doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9193-y. Epub 2007 Apr 21. Microb Ecol. 2007. PMID: 17450395
Cited by
-
Dynamic distribution of gallbladder microbiota in rabbit at different ages and health states.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 4;14(2):e0211828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211828. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30716131 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Exogenous Lysozyme Supplementation on Growth Performance, Caecal Fermentation and Microbiota, and Blood Constituents in Growing Rabbits.Animals (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;12(7):899. doi: 10.3390/ani12070899. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35405887 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary fiber levels on bacterial composition with age in the cecum of meat rabbits.Microbiologyopen. 2019 May;8(5):e00708. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.708. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Microbiologyopen. 2019. PMID: 30085417 Free PMC article.
-
The use of non-rodent model species in microbiota studies.Lab Anim. 2019 Jun;53(3):259-270. doi: 10.1177/0023677219834593. Lab Anim. 2019. PMID: 31096881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of coprophagy prevention on the growth performance, serum biochemistry, and intestinal microbiome of rabbits.BMC Microbiol. 2023 May 10;23(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02869-y. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37165350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abecia L, Fondevila M, Balcells J, Edwards JE, Newbold CJ, McEwan NR. Molecular profiling of bacterial species in the rabbit caecum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005;244:111–115. - PubMed
-
- Azard A. 2006. Gestion technico-économique des éleveurs de lapin de chair – RENACEB et RENALAP – résultats 2006. In “ITAVI technical report”. http://itavi.asso.fr/economie/references/synthesegtelapin2006.pdf.
-
- Bennegadi N, Fonty G, Millet L, Gidenne T, Licois D. Effects of age and dietary fibre level on caecal microbial communities of conventional and specific pathogen-free rabbits. Microb Ecol Health D. 2003;5:23–32.
-
- Boulahrouf A, Fonty G, Gouet P. Establishment, counts, and identification of the fibrolytic microflora in the digestive tract of rabbit. Influence of feed cellulose content. Curr Microbiol. 1991;22:21–25. - PubMed
-
- Carabaño R, Badiola I, Licois D, Gidenne T. The digestive ecosystem and its control through nutritional or feeding strategies. In: Coudert P, Maertens L, editors. Recent Advances in Rabbit Sciences. Melle, Belgium: COST (ESF) and ILVO; 2006. pp. 211–228.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

