Caveolin-3 regulates myostatin signaling. Mini-review
- PMID: 19108573
- PMCID: PMC2859606
Caveolin-3 regulates myostatin signaling. Mini-review
Abstract
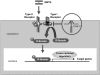
Caveolins, components of the uncoated invaginations of plasma membrane, regulate signal transduction and vesicular trafflicking. Loss of caveolin-3, resulting from dominant negative mutations of caveolin-3 causes autosomal dominant limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) 1C and autosomal dominant rippling muscle disease (AD-RMD). Myostatin, a member of the muscle-specific transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta superfamily, negatively regulates skeletal muscle volume. Herein we review caveolin-3 suppressing of activation of type I myostatin receptor, thereby inhibiting subsequent intracellular signaling. In addition, a mouse model of LGMD1C has shown atrophic myopathy with enhanced myostatin signaling. Myostatin inhibition ameliorates muscular phenotype in the model mouse, accompanied by normalized myostatin signaling. Enhanced myostatin signaling by caveolin-3 mutation in human may contribute to the pathogenesis of LGMD1C. Therefore, myostatin inhibition therapy may be a promising treatment for patients with LGMD1C. More recent studies concerning regulation of TGF-beta superfamily signaling by caveolins have provided new insights into the pathogenesis of several human diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Muscular atrophy of caveolin-3-deficient mice is rescued by myostatin inhibition.J Clin Invest. 2006 Nov;116(11):2924-34. doi: 10.1172/JCI28520. Epub 2006 Oct 12. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 17039257 Free PMC article.
-
An inhibitor of transforming growth factor beta type I receptor ameliorates muscle atrophy in a mouse model of caveolin 3-deficient muscular dystrophy.Lab Invest. 2012 Aug;92(8):1100-14. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2012.78. Epub 2012 May 14. Lab Invest. 2012. PMID: 22584670
-
The Inhibitory Core of the Myostatin Prodomain: Its Interaction with Both Type I and II Membrane Receptors, and Potential to Treat Muscle Atrophy.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 30;10(7):e0133713. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133713. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26226340 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolinopathies: from the biology of caveolin-3 to human diseases.Eur J Hum Genet. 2010 Feb;18(2):137-45. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.103. Epub 2009 Jul 8. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 19584897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolae and caveolin-3 in muscular dystrophy.Trends Mol Med. 2001 Oct;7(10):435-41. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4914(01)02105-0. Trends Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11597517 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Membrane Repair: A Central Process for Maintaining Cellular Homeostasis.Physiology (Bethesda). 2015 Nov;30(6):438-48. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00019.2015. Physiology (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26525343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New relationship of E2F1 and BNIP3 with caveolin-1 in lung cancer-associated fibroblasts.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jun;11(6):1369-1371. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13408. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32212370 Free PMC article.
-
Sparing of muscle mass and function by passive loading in an experimental intensive care unit model.J Physiol. 2013 Mar 1;591(5):1385-402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.248724. Epub 2012 Dec 24. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23266938 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle wasting and the temporal gene expression pattern in a novel rat intensive care unit model.BMC Genomics. 2011 Dec 13;12:602. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-602. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22165895 Free PMC article.
-
The intriguing regulators of muscle mass in sarcopenia and muscular dystrophy.Front Aging Neurosci. 2014 Aug 29;6:230. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00230. eCollection 2014. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25221510 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parton RG. Caveolae-from ultrastructure to molecular mechanism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003;4:162-7. - PubMed
-
- Parton RG, Hanzal-Bayer M, Hancock JF. Biogenesis of caveolae: a structural model for caveolin-induced domain formation. J Cell Sci 2006;119:787-96. - PubMed
-
- Parton GP, Simonds K. The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007;8:185-94. - PubMed
-
- Razani B, Schlegel A, Lisanti MP. Caveolin proteins in signaling, oncogenic transformation and muscular dystrophy. J Cell Sci 2000;113:2103-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
