Mammary epithelial-specific ablation of the focal adhesion kinase suppresses mammary tumorigenesis by affecting mammary cancer stem/progenitor cells
- PMID: 19147559
- PMCID: PMC3039129
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3078
Mammary epithelial-specific ablation of the focal adhesion kinase suppresses mammary tumorigenesis by affecting mammary cancer stem/progenitor cells
Abstract
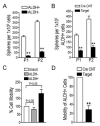
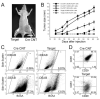
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) has been implicated in the development of cancers, including those of the breast. Nevertheless, the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which FAK promotes mammary tumorigenesis in vivo are not well understood. Here, we show that _targeted deletion of FAK in mouse mammary epithelium significantly suppresses mammary tumorigenesis in a well-characterized breast cancer model. Ablation of FAK leads to the depletion of a subset of bipotent cells in the tumor that express both luminal marker keratin 8/18 and basal marker keratin 5. Using mammary stem/progenitor markers, including aldehyde dehydrogenase, CD24, CD29, and CD61, we further revealed that ablation of FAK reduced the pool of cancer stem/progenitor cells in primary tumors of FAK-_targeted mice and impaired their self-renewal and migration in vitro. Finally, through transplantation in NOD-SCID mice, we found that cancer stem/progenitor cells isolated from FAK-_targeted mice have compromised tumorigenicity and impaired maintenance in vivo. Together, these results show a novel function of FAK in maintaining the mammary cancer stem/progenitor cell population and provide a novel mechanism by which FAK may promote breast cancer development and progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Function of focal adhesion kinase scaffolding to mediate endophilin A2 phosphorylation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mammary cancer stem cell activities in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 1;288(5):3322-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.420497. Epub 2012 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23255596 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct FAK activities determine progenitor and mammary stem cell characteristics.Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 1;73(17):5591-602. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1351. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23832665 Free PMC article.
-
Mammary gland-specific ablation of focal adhesion kinase reduces the incidence of p53-mediated mammary tumour formation.Br J Cancer. 2014 May 27;110(11):2747-55. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.219. Epub 2014 May 8. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24809783 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin signaling through FAK in the regulation of mammary stem cells and breast cancer.IUBMB Life. 2010 Apr;62(4):268-76. doi: 10.1002/iub.303. IUBMB Life. 2010. PMID: 20101634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cells in mammary development and carcinogenesis: implications for prevention and treatment.Stem Cell Rev. 2005;1(3):207-13. doi: 10.1385/SCR:1:3:207. Stem Cell Rev. 2005. PMID: 17142857 Review.
Cited by
-
FAK loss reduces BRAFV600E-induced ERK phosphorylation to promote intestinal stemness and cecal tumor formation.Elife. 2024 Jun 26;13:RP94605. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94605. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38921956 Free PMC article.
-
GLI1 regulates a novel neuropilin-2/α6β1 integrin based autocrine pathway that contributes to breast cancer initiation.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Apr;5(4):488-508. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201202078. Epub 2013 Feb 21. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23436775 Free PMC article.
-
β1-integrins signaling and mammary tumor progression in transgenic mouse models: implications for human breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):229. doi: 10.1186/bcr2905. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22264244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRD4 modulates vulnerability of triple-negative breast cancer to _targeting of integrin-dependent signaling pathways.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Dec;43(6):1049-1066. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00537-1. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 33006750 Free PMC article.
-
How integrins control breast biology.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;25(5):633-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23886475 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kordon EC, Smith GH. An entire functional mammary gland may comprise the progeny from a single cell. Development. 1998;125:1921–30. - PubMed
-
- Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Mammary Stem Cells and Mammopoiesis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9798–801. - PubMed
-
- Shackleton M, Vaillant Fo, Simpson KJ, et al. Generation of a functional mammary gland from a single stem cell. Nature. 2006;439:84–8. - PubMed
-
- Stingl J, Eirew P, Ricketson I, et al. Purification and unique properties of mammary epithelial stem cells. Nature. 2006;439:993–7. - PubMed
-
- Asselin-Labat ML, Shackleton M, Stingl J, et al. Steroid hormone receptor status of mouse mammary stem cells. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2006;98:1011–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

