Amplification-free Illumina sequencing-library preparation facilitates improved mapping and assembly of (G+C)-biased genomes
- PMID: 19287394
- PMCID: PMC2664327
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1311
Amplification-free Illumina sequencing-library preparation facilitates improved mapping and assembly of (G+C)-biased genomes
Abstract
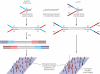
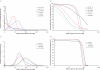
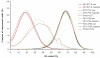
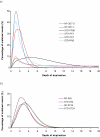
Amplification artifacts introduced during library preparation for the Illumina Genome Analyzer increase the likelihood that an appreciable proportion of these sequences will be duplicates and cause an uneven distribution of read coverage across the _targeted sequencing regions. As a consequence, these unfavorable features result in difficulties in genome assembly and variation analysis from the short reads, particularly when the sequences are from genomes with base compositions at the extremes of high or low G+C content. Here we present an amplification-free method of library preparation, in which the cluster amplification step, rather than the PCR, enriches for fully ligated template strands, reducing the incidence of duplicate sequences, improving read mapping and single nucleotide polymorphism calling and aiding de novo assembly. We illustrate this by generating and analyzing DNA sequences from extremely (G+C)-poor (Plasmodium falciparum), (G+C)-neutral (Escherichia coli) and (G+C)-rich (Bordetella pertussis) genomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimizing Illumina next-generation sequencing library preparation for extremely AT-biased genomes.BMC Genomics. 2012 Jan 3;13:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-1. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22214261 Free PMC article.
-
Amplification-free library preparation for paired-end Illumina sequencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;733:257-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-089-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21431776
-
Sequencing of high G+C microbial genomes using the ultrafast pyrosequencing technology.J Biotechnol. 2011 Aug 20;155(1):68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.04.010. Epub 2011 Apr 23. J Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21536083
-
De novo sequencing of plant genomes using second-generation technologies.Brief Bioinform. 2009 Nov;10(6):609-18. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbp039. Brief Bioinform. 2009. PMID: 19933209 Review.
-
Application of hybridization techniques to genome mapping and sequencing.Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):79-83. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90229-1. Trends Genet. 1994. PMID: 8178368 Review.
Cited by
-
FOXA1 defines cancer cell specificity.Sci Adv. 2016 Mar 18;2(3):e1501473. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501473. eCollection 2016 Mar. Sci Adv. 2016. PMID: 27034986 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Verification of an Economical Method of Custom _target Library Construction.ACS Omega. 2020 May 29;5(22):13087-13095. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01014. eCollection 2020 Jun 9. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32548494 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Plasmodium falciparum diversity in natural infections by deep sequencing.Nature. 2012 Jul 19;487(7407):375-9. doi: 10.1038/nature11174. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22722859 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of a nutritional endosymbiont by glyphosate abolishes mutualistic benefit on cuticle synthesis in Oryzaephilus surinamensis.Commun Biol. 2021 May 11;4(1):554. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02057-6. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33976379 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotype-specific assembly of shattered chromosomes in esophageal adenocarcinomas.Cell Genom. 2024 Feb 14;4(2):100484. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100484. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 38232733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goman M, et al. The establishment of genomic DNA libraries for the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum and identification of individual clones by hybridisation. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982;5:391–400. - PubMed
-
- Camargo AA, Fischer K, Lanzer M, del Portillo HA. Construction and characterization of a Plasmodium vivax genomic library in yeast artificial chromosomes. Genomics. 1997;42:467–473. - PubMed
-
- de Bruin D, Lanzer M, Ravetch JV. Characterization of yeast artificial chromosomes from Plasmodium falciparum: construction of a stable, representative library and cloning of telomeric DNA fragments. Genomics. 1992;14:332–339. - PubMed
-
- Triglia T, Kemp DJ. Large fragments of Plasmodium falciparum DNA can be stable when cloned in yeast artificial chromosomes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991;44:207–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

