An integrin-alpha4-14-3-3zeta-paxillin ternary complex mediates localised Cdc42 activity and accelerates cell migration
- PMID: 19401330
- PMCID: PMC2680104
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.049130
An integrin-alpha4-14-3-3zeta-paxillin ternary complex mediates localised Cdc42 activity and accelerates cell migration
Abstract
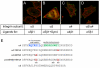
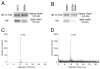
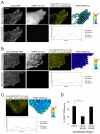
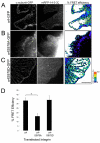
Alpha4 integrins are used by leukocytes and neural crest derivatives for adhesion and migration during embryogenesis, immune responses and tumour invasion. The pro-migratory activity of alpha4 integrin is mediated in part through the direct binding of the cytoplasmic domain to paxillin. Here, using intermolecular FRET and biochemical analyses, we report a novel interaction of the alpha4 integrin cytoplasmic domain with 14-3-3zeta. This interaction depends on serine phosphorylation of alpha4 integrin at a site (S978) distinct from that which regulates paxillin binding (S988). Using a combination of metabolic labelling and _targeted mass spectrometry by multiple reaction monitoring we demonstrate the low stoichiometry phosphorylation of S978. The interaction between alpha4 integrin and 14-3-3zeta is enhanced by the direct association between 14-3-3zeta and paxillin, resulting in the formation of a ternary complex that stabilises the recruitment of each component. Although pair-wise interaction between alpha4 integrin and paxillin is sufficient for normal Rac1 regulation, the integrity of the ternary complex is essential for focused Cdc42 activity at the lamellipodial leading edge and directed cell movement. Taken together, these data identify a key signalling nexus mediating alpha4 integrin-dependent migration.
Figures
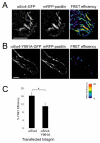
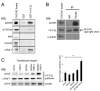
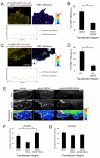
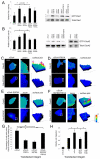
Similar articles
-
Spatial restriction of alpha4 integrin phosphorylation regulates lamellipodial stability and alpha4beta1-dependent cell migration.J Cell Biol. 2003 Aug 18;162(4):731-41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200304031. Epub 2003 Aug 11. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12913113 Free PMC article.
-
Association between α4 integrin cytoplasmic tail and non-muscle myosin IIA regulates cell migration.J Cell Sci. 2011 Feb 1;124(Pt 3):483-92. doi: 10.1242/jcs.074211. Epub 2011 Jan 11. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21224395 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of paxillin to alpha4 integrins modifies integrin-dependent biological responses.Nature. 1999 Dec 9;402(6762):676-81. doi: 10.1038/45264. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10604475
-
The role of the alpha4 integrin-paxillin interaction in regulating leukocyte trafficking.Exp Mol Med. 2006 Jun 30;38(3):191-5. doi: 10.1038/emm.2006.23. Exp Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16819276 Review.
-
New approaches to blockade of alpha4-integrins, proven therapeutic _targets in chronic inflammation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 30;72(11):1460-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.06.014. Epub 2006 Jul 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16870156 Review.
Cited by
-
14-3-3θ facilitates plasma membrane delivery and function of mechanosensitive connexin 43 hemichannels.J Cell Sci. 2014 Jan 1;127(Pt 1):137-46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.133553. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24163432 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Rho GTPases and 14-3-3 Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 15;18(10):2148. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102148. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29036929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paxillin and Hic-5 interaction with vinculin is differentially regulated by Rac1 and RhoA.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037990. Epub 2012 May 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22629471 Free PMC article.
-
The ATP-dependent RNA helicase, DDX42 interacts with paxillin and regulates apoptosis and polarization of Ba/F3 cells.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2019 Jan 21;23(1):1-9. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2019.1567580. eCollection 2019 Feb. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2019. PMID: 30834153 Free PMC article.
-
Paxillin inhibits HDAC6 to regulate microtubule acetylation, Golgi structure, and polarized migration.J Cell Biol. 2014 Aug 4;206(3):395-413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201403039. Epub 2014 Jul 28. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25070956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitken, A. (2006). 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin. Cancer Biol. 16, 162-172. - PubMed
-
- Alon, R., Feigelson, S. W., Manevich, E., Rose, D. M., Schmitz, J., Overby, D. R., Winter, E., Grabovsky, V., Shinder, V., Matthews, B. D. et al. (2005). Alpha4beta1-dependent adhesion strengthening under mechanical strain is regulated by paxillin association with the alpha4-cytoplasmic domain. J. Cell Biol. 171, 1073-1084. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, D. E. (2007). Natalizumab: overview of its pharmacology and safety. Rev. Gastroenterol. Disord. 7, 38-46. - PubMed
-
- Bass, M. D., Roach, K. A., Morgan, M. R., Mostafavi-Pour, Z., Schoen, T., Muramatsu, T., Mayer, U., Ballestrem, C., Spatz, J. P. and Humphries, M. J. (2007). Syndecan-4-dependent Rac1 regulation determines directional migration in response to the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 177, 527-538. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

