Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 alters estrogen receptor activity and estrogen-responsive gene expression
- PMID: 19460860
- PMCID: PMC2737565
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0093
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 alters estrogen receptor activity and estrogen-responsive gene expression
Abstract
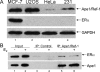
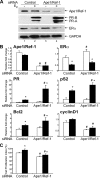
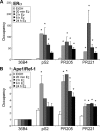
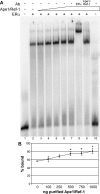
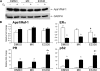
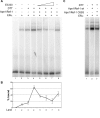
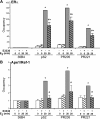
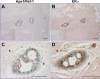
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 or redox factor-1 (Ape1/Ref-1) is a pleiotropic cellular protein involved in DNA repair and, through its redox activity, enhances the binding of a select group of transcription factors to their cognate recognition sequences in DNA. Thus, we were intrigued when we identified Ape1/Ref-1 and a number of DNA repair and oxidative stress proteins in a complex associated with the DNA-bound estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha). Because Ape1/Ref-1 interacts with a number of transcription factors and influences their activity, we determined whether it might also influence ERalpha activity. We found that endogenously expressed Ape1/Ref-1 and ERalpha from MCF-7 human breast cancer cells interact and that Ape1/Ref-1 enhances the interaction of ERalpha with estrogen-response elements (EREs) in DNA. More importantly, Ape1/Ref-1 alters expression of the endogenous, estrogen-responsive progesterone receptor and pS2 genes in MCF-7 cells and associates with ERE-containing regions of these genes in native chromatin. Interestingly, knocking down Ape1/Ref-1 expression or inhibiting its redox activity with the small molecule inhibitor E3330 enhances estrogen responsiveness of the progesterone receptor and pS2 genes but does not alter the expression of the constitutively active 36B4 gene. Additionally, the reduced form of Ape1/Ref-1 increases and E3330 limits ERalpha-ERE complex formation in vitro and in native chromatin. Our studies demonstrate that Ape1/Ref-1 mediates its gene-specific effects, in part, by associating with endogenous, estrogen-responsive genes and that the redox activity of Ape1/Ref-1 is instrumental in altering estrogen-responsive gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitors of nuclease and redox activity of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox effector factor 1 (APE1/Ref-1).Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 May 1;25(9):2531-2544. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.028. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28161249 Review.
-
Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Factor-1 (Ape1/Ref-1) Modulates Antigen Presenting Cell-mediated T Helper Cell Type 1 Responses.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23672-23680. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.742353. Epub 2016 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27637330 Free PMC article.
-
APE1/Ref-1 enhances DNA binding activity of mutant p53 in a redox-dependent manner.Oncol Rep. 2014 Feb;31(2):901-9. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2892. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24297337
-
Inhibition of the redox function of APE1/Ref-1 in myeloid leukemia cell lines results in a hypersensitive response to retinoic acid-induced differentiation and apoptosis.Exp Hematol. 2010 Dec;38(12):1178-88. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.08.011. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Exp Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20826193 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA base excision repair protein Ape1/Ref-1 as a therapeutic and chemopreventive _target.Mol Aspects Med. 2007 Jun-Aug;28(3-4):375-95. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 May 3. Mol Aspects Med. 2007. PMID: 17560642 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoscale Interaction of Endonuclease APE1 with DNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5145. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105145. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791183 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-disulfide isomerase regulates the thyroid hormone receptor-mediated gene expression via redox factor-1 through thiol reduction-oxidation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):1706-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.365239. Epub 2012 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23148211 Free PMC article.
-
Apurinic/Apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 regulates inflammatory response in macrophages.Anticancer Res. 2011 Feb;31(2):379-85. Anticancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21378315 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of choroidal neovascularization through inhibition of APE1/Ref-1 redox activity.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Jun 26;55(7):4461-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14451. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24970265 Free PMC article.
-
17β-Estradiol alters oxidative damage and oxidative stress response protein expression in the mouse mammary gland.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016 May 5;426:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.02.007. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26872614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Webster KA, Prentice H, Bishopric NH 2001 Oxidation of zinc finger transcription factors: physiological consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal 3:535–548 - PubMed
-
- Jayaraman L, Murthy KG, Zhu C, Curran T, Xanthoudakis S, Prives C 1997 Identification of redox/repair protein Ref-1 as a potent activator of p53. Genes Dev 11:558–570 - PubMed
-
- Evans AR, Limp-Foster M, Kelley MR 2000 Going APE over ref-1. Mutat Res 461:83–108 - PubMed
-
- Sweasy JB, Lang T, DiMaio D 2006 Is base excision repair a tumor suppressor mechanism? Cell Cycle 5:250–259 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

