Large-scale analysis of antisense transcription in wheat using the Affymetrix GeneChip Wheat Genome Array
- PMID: 19480707
- PMCID: PMC2694213
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-253
Large-scale analysis of antisense transcription in wheat using the Affymetrix GeneChip Wheat Genome Array
Abstract
Background: Natural antisense transcripts (NATs) are transcripts of the opposite DNA strand to the sense-strand either at the same locus (cis-encoded) or a different locus (trans-encoded). They can affect gene expression at multiple stages including transcription, RNA processing and transport, and translation. NATs give rise to sense-antisense transcript pairs and the number of these identified has escalated greatly with the availability of DNA sequencing resources and public databases. Traditionally, NATs were identified by the alignment of full-length cDNAs or expressed sequence tags to genome sequences, but an alternative method for large-scale detection of sense-antisense transcript pairs involves the use of microarrays. In this study we developed a novel protocol to assay sense- and antisense-strand transcription on the 55 K Affymetrix GeneChip Wheat Genome Array, which is a 3' in vitro transcription (3'IVT) expression array. We selected five different tissue types for assay to enable maximum discovery, and used the 'Chinese Spring' wheat genotype because most of the wheat GeneChip probe sequences were based on its genomic sequence. This study is the first report of using a 3'IVT expression array to discover the expression of natural sense-antisense transcript pairs, and may be considered as proof-of-concept.
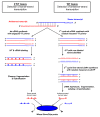
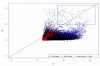
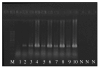
Results: By using alternative _target preparation schemes, both the sense- and antisense-strand derived transcripts were labeled and hybridized to the Wheat GeneChip. Quality assurance verified that successful hybridization did occur in the antisense-strand assay. A stringent threshold for positive hybridization was applied, which resulted in the identification of 110 sense-antisense transcript pairs, as well as 80 potentially antisense-specific transcripts. Strand-specific RT-PCR validated the microarray observations, and showed that antisense transcription is likely to be tissue specific. For the annotated sense-antisense transcript pairs, analysis of the gene ontology terms showed a significant over-representation of transcripts involved in energy production. These included several representations of ATP synthase, photosystem proteins and RUBISCO, which indicated that photosynthesis is likely to be regulated by antisense transcripts.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated the novel use of an adapted labeling protocol and a 3'IVT GeneChip array for large-scale identification of antisense transcription in wheat. The results show that antisense transcription is relatively abundant in wheat, and may affect the expression of valuable agronomic phenotypes. Future work should select potentially interesting transcript pairs for further functional characterization to determine biological activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of novel endogenous antisense transcripts by DNA microarray analysis _targeting complementary strand of annotated genes.BMC Genomics. 2009 Aug 22;10:392. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-392. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19698135 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense transcripts with rice full-length cDNAs.Genome Biol. 2003;5(1):R5. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-5-1-r5. Epub 2003 Dec 11. Genome Biol. 2003. PMID: 14709177 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed sense and antisense transcript pairs in breast epithelial tissues.BMC Genomics. 2009 Jul 17;10:324. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-324. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19615061 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic search for natural antisense transcripts in eukaryotes (review).Int J Mol Med. 2005 Feb;15(2):197-203. Int J Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15647831 Review.
-
Strategies to identify natural antisense transcripts.Biochimie. 2017 Jan;132:131-151. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 27894947 Review.
Cited by
-
Large-scale transcriptome comparison reveals distinct gene activations in wheat responding to stripe rust and powdery mildew.BMC Genomics. 2014 Oct 15;15(1):898. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-898. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25318379 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and functional prediction of novel and fungi-responsive lincRNAs in Triticum aestivum.BMC Genomics. 2016 Mar 15;17:238. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2570-0. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26980266 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression in incompatible interaction between wheat and stripe rust fungus revealed by cDNA-AFLP and comparison to compatible interaction.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Jan 12;10:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20067621 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Molecular Mechanisms of Durable and Non-durable Resistance to Stripe Rust in Wheat Using a Transcriptomics Approach.Curr Genomics. 2013 Apr;14(2):111-26. doi: 10.2174/1389202911314020004. Curr Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24082821 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of alternative RNA labeling protocols for transcript profiling with Arabidopsis AGRONOMICS1 tiling arrays.Plant Methods. 2012 Jun 13;8(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-8-18. Plant Methods. 2012. PMID: 22694760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu C, Jeong DH, Kulkarni K, Pillay M, Nobuta K, German R, Thatcher SR, Maher C, Zhang L, Ware D, et al. Genome-wide analysis for discovery of rice microRNAs reveals natural antisense microRNAs (nat-miRNAs) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:4951–4956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708743105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

