SP-A preserves airway homeostasis during Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in mice
- PMID: 19494306
- PMCID: PMC3656438
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900452
SP-A preserves airway homeostasis during Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in mice
Erratum in
-
Correction: SP-A Preserves Airway Homeostasis during Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection in Mice.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 15;195(6):2917-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501597. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26342104 No abstract available.
Abstract
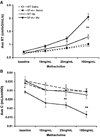
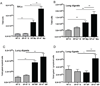
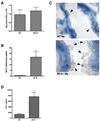
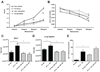
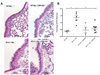
The lung is constantly challenged during normal breathing by a myriad of environmental irritants and infectious insults. Pulmonary host defense mechanisms maintain homeostasis between inhibition/clearance of pathogens and regulation of inflammatory responses that could injure the airway epithelium. One component of this defense mechanism, surfactant protein-A (SP-A), exerts multifunctional roles in mediating host responses to inflammatory and infectious agents. SP-A has a bacteriostatic effect on Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Mp), which occurs by binding surface disaturated phosphatidylglycerols. SP-A can also bind the Mp membrane protein, MPN372. In this study, we investigated the role of SP-A during acute phase pulmonary infection with Mp using mice deficient in SP-A. Biologic responses, inflammation, and cellular infiltration, were much greater in Mp infected SP-A(-/-) mice than wild-type mice. Likewise, physiologic responses (airway hyperresponsiveness and lung compliance) to Mp infection were more severely affected in SP-A(-/-) mice. Both Mp-induced biologic and physiologic changes were attenuated by pharmacologic inhibition of TNF-alpha. Our findings demonstrate that SP-A is vital to preserving lung homeostasis and host defense to this clinically relevant strain of Mp by curtailing inflammatory cell recruitment and limiting an overzealous TNF-alpha response.
Figures
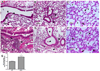
Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2019 Nov 7;84(216):60097-60098. Fed Regist. 2019. PMID: 37547121 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Mast cell TNF receptors regulate responses to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in surfactant protein A (SP-A)-/- mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Jul;130(1):205-14.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22502799 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant protein-A suppresses eosinophil-mediated killing of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in allergic lungs.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032436. Epub 2012 Feb 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384248 Free PMC article.
-
A 20-Mer Peptide Derived from the Lectin Domain of SP-A2 Decreases Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Production during Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection.Infect Immun. 2020 Aug 19;88(9):e00099-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00099-20. Print 2020 Aug 19. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32513852 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation in SP-A2 leads to differential binding to Mycoplasma pneumoniae membranes and regulation of host responses.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 15;194(12):6123-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500104. Epub 2015 May 8. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25957169 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Collectins link innate and adaptive immunity in allergic airway disease.Innate Immun. 2010 Jun;16(3):183-90. doi: 10.1177/1753425910368446. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Innate Immun. 2010. PMID: 20418258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Emerging Roles of Surfactant Protein-A in Asthma.J Clin Cell Immunol. 2018;9(4):553. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.1000553. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30123671 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of innate immune variants of surfactant protein-A1 (SFTPA1) and SP-A2 (SFTPA2) in airway function after Klebsiella pneumoniae infection and sex differences.Respir Res. 2018 Feb 3;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0723-1. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29394894 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in the cellular composition and epithelial organization of the mouse trachea.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 27;9(3):e93496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093496. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24675804 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the pathogenesis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2016 Nov;14(5):4030-4036. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5765. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27667580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-associated differentiation marker is a novel SP-A-associated transmembrane protein whose expression on airway epithelial cells correlates with asthma severity.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 3;11(1):23392. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02869-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34862427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clements JA. Surface tension of lung extracts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957;95:170–172. - PubMed
-
- Pattle RE. Properties, function and origin of the alveolar lining layer. Nature. 1955;175:1125–1126. - PubMed
-
- Borron P, McCormack FX, Elhalwagi BM, Chroneos ZC, Lewis JF, Zhu S, Wright JR, Shepherd VL, Possmayer F, Inchley K, Fraher LJ. Surfactant protein A inhibits T cell proliferation via its collagen-like tail and a 210-kDa receptor. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:L679–L686. - PubMed
-
- Brinker KG, Garner H, Wright JR. Surfactant protein A modulates the differentiation of murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;284:L232–L241. - PubMed
-
- Stamme C, Walsh E, Wright JR. Surfactant protein A differentially regulates IFN-gamma- and LPS-induced nitrite production by rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000;23:772–779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

