The polarity protein Par1b/EMK/MARK2 regulates T cell receptor-induced microtubule-organizing center polarization
- PMID: 19553522
- PMCID: PMC2837933
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803887
The polarity protein Par1b/EMK/MARK2 regulates T cell receptor-induced microtubule-organizing center polarization
Abstract
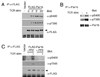
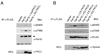
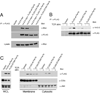
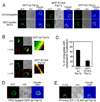
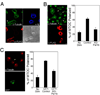
Engagement of a T cell to an APC induces the formation of an immunological synapse as well as reorientation of the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) toward the APC. How signals emanating from the TCR induce MTOC polarization is not known. One group of proteins known to play a critical role in asymmetric cell division and cell polarization is the partitioning defective (Par) family of proteins. In this study we found that Par1b, a member of the Par family of proteins, was inducibly phosphorylated following TCR stimulation. This phosphorylation resulted in 14-3-3 protein binding and caused the relocalization of Par1b from the membrane into the cytoplasm. Because a dominant-negative form of Par1b blocked TCR-induced MTOC polarization, our data suggest that Par1b functions in the establishment of T cell polarity following engagement to an APC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From lipid second messengers to molecular motors: microtubule-organizing center reorientation in T cells.Immunol Rev. 2013 Nov;256(1):95-106. doi: 10.1111/imr.12116. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24117815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linker for activation of T cells, zeta-associated protein-70, and Src homology 2 domain-containing leukocyte protein-76 are required for TCR-induced microtubule-organizing center polarization.J Immunol. 2003 Jul 15;171(2):860-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.2.860. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12847255
-
The Rap1-cofilin-1 pathway coordinates actin reorganization and MTOC polarization at the B cell immune synapse.J Cell Sci. 2017 Mar 15;130(6):1094-1109. doi: 10.1242/jcs.191858. Epub 2017 Feb 6. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28167682
-
HTLV-1-Tax and ICAM-1 act on T-cell signal pathways to polarize the microtubule-organizing center at the virological synapse.Blood. 2009 Jul 30;114(5):1016-25. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-136770. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19494354
-
Regulation of microtubule-organizing center orientation and actomyosin cytoskeleton rearrangement during immune interactions.Immunol Rev. 2002 Nov;189:84-97. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2002.18908.x. Immunol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12445267 Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphocyte polarity, the immunological synapse and the scope of biological analogy.Bioarchitecture. 2011 Jul;1(4):180-185. doi: 10.4161/bioa.1.4.17594. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Bioarchitecture. 2011. PMID: 22069511 Free PMC article.
-
From lipid second messengers to molecular motors: microtubule-organizing center reorientation in T cells.Immunol Rev. 2013 Nov;256(1):95-106. doi: 10.1111/imr.12116. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24117815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cell polarity kinase Par1b/MARK2 activation selects specific NF-kB transcripts via phosphorylation of core mediator Med17/TRAP80.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Apr 15;32(8):690-702. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-10-0646. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33596087 Free PMC article.
-
The immunological synapse: a focal point for endocytosis and exocytosis.J Cell Biol. 2010 May 3;189(3):399-406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201002027. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20439993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune synapse: conductor of orchestrated organelle movement.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;24(1):61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.09.005. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24119664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Macara IG. Parsing the polarity code. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:220–231. - PubMed
-
- Kemphues KJ, Priess JR, Morton DG, Cheng NS. Identification of genes required for cytoplasmic localization in early C. elegans embryos. Cell. 1988;52:311–320. - PubMed
-
- Hurd TW, Gao L, Roh MH, Macara IG, Margolis B. Direct interaction of two polarity complexes implicated in epithelial tight junction assembly. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:137–142. - PubMed
-
- Shi SH, Jan LY, Jan YN. Hippocampal neuronal polarity specified by spatially localized mPar3/mPar6 and PI 3-kinase activity. Cell. 2003;112:63–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

