von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease ADAMTS13 reduces ischemic brain injury in experimental stroke
- PMID: 19687510
- PMCID: PMC2759655
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-213264
von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease ADAMTS13 reduces ischemic brain injury in experimental stroke
Abstract
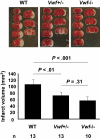
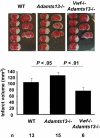
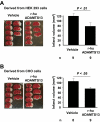
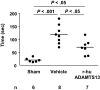
Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability. The only therapy available is recombinant tissue plasminogen activator, but side effects limit its use. Platelets play a crucial role during stroke, and the inflammatory reaction promotes neurodegeneration. von Willebrand factor (VWF), an adhesion molecule for platelets, is elevated in patients with acute stroke. The activity of VWF is modulated by ADAMTS13 (a disintegrin-like and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type I repeats-13) that cleaves VWF to smaller less-active forms. We recently documented that ADAMTS13 negatively regulates both thrombosis and inflammation. We report that deficiency or reduction of VWF reduces infarct volume up to 2-fold after focal cerebral ischemia in mice, thus showing the importance of VWF in stroke injury. In contrast, ADAMTS13 deficiency results in larger infarctions, but only in mice that have VWF. Importantly, infusion of a high dose of recombinant human ADAMTS13 into a wild-type mouse immediately before reperfusion reduces infarct volume and improves functional outcome without producing cerebral hemorrhage. Furthermore, recombinant ADAMTS13 did not enhance bleeding in a hemorrhagic stroke model. Our findings show the importance of VWF in regulating infarction and suggest that recombinant ADAMTS13 could be considered as a new therapeutic agent for prevention and/or treatment of stroke.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ADAMTS13 reduces VWF-mediated acute inflammation following focal cerebral ischemia in mice.J Thromb Haemost. 2012 Aug;10(8):1665-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04822.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22712744 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Cell-Derived von Willebrand Factor Is the Major Determinant That Mediates von Willebrand Factor-Dependent Acute Ischemic Stroke by Promoting Postischemic Thrombo-Inflammation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Sep;36(9):1829-37. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307660. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27444201 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant ADAMTS13 reduces tissue plasminogen activator-induced hemorrhage after stroke in mice.Ann Neurol. 2013 Feb;73(2):189-98. doi: 10.1002/ana.23762. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Ann Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23280993
-
Interplay between ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor in inherited and acquired thrombotic microangiopathies.Semin Hematol. 2005 Jan;42(1):56-62. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2004.09.008. Semin Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15662617 Review.
-
Von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 in arterial thrombosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Blood Rev. 2014 Jul;28(4):167-78. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Blood Rev. 2014. PMID: 24825749 Review.
Cited by
-
ADAMTS13 predicts renal and cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetic patients and response to therapy.Diabetes. 2013 Oct;62(10):3599-609. doi: 10.2337/db13-0530. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23733198 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Platelets and Nitric Oxide Biotransformation in Ischemic Stroke: A Translative Review from Bench to Bedside.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Aug 28;2020:2979260. doi: 10.1155/2020/2979260. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32908630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAMTS13 Endopeptidase Protects against Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor-Induced Thrombotic Microangiopathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jan;27(1):120-31. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014121165. Epub 2015 Jun 2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26038528 Free PMC article.
-
von Willebrand factor: an emerging _target in stroke therapy.Stroke. 2012 Feb;43(2):599-606. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.628867. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Stroke. 2012. PMID: 22180250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Plasma Levels of ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Patients Undergoing Elective Joint Arthroplasty.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 30;11(21):6436. doi: 10.3390/jcm11216436. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36362664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics - 2009 Update. Dallas TX: American Heart Association; 2009.
-
- Hacke W, Brott T, Caplan L, et al. Thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: controlled trials and clinical experience. Neurology. 1999;53(7) suppl 4:S3–S14. - PubMed
-
- del Zoppo GJ. Antithrombotic treatments in acute ischemic stroke. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82(2):938–946. - PubMed
-
- Denis CV, Wagner DD. Platelet adhesion receptors and their ligands in mouse models of thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27(2):728–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

