Effects of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on gene expression profiles in the liver of schizophrenia subjects
- PMID: 19758435
- PMCID: PMC2749837
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-9-57
Effects of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on gene expression profiles in the liver of schizophrenia subjects
Abstract
Background: Although much progress has been made on antipsychotic drug development, precise mechanisms behind the action of typical and atypical antipsychotics are poorly understood.
Methods: We performed genome-wide expression profiling to study effects of typical antipsychotics and atypical antipsychotics in the postmortem liver of schizophrenia patients using microarrays (Affymetrix U133 plus2.0). We classified the subjects into typical antipsychotics (n = 24) or atypical antipsychotics (n = 26) based on their medication history, and compared gene expression profiles with unaffected controls (n = 34). We further analyzed individual antipsychotic effects on gene expression by sub-classifying the subjects into four major antipsychotic groups including haloperidol, phenothiazines, olanzapine and risperidone.
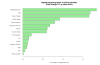
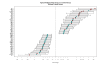
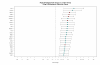
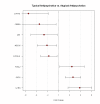
Results: Typical antipsychotics affected genes associated with nuclear protein, stress responses and phosphorylation, whereas atypical antipsychotics affected genes associated with golgi/endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasm transport. Comparison between typical antipsychotics and atypical antipsychotics further identified genes associated with lipid metabolism and mitochondrial function. Analyses on individual antipsychotics revealed a set of genes (151 transcripts, FDR adjusted p < 0.05) that are differentially regulated by four antipsychotics, particularly by phenothiazines, in the liver of schizophrenia patients.
Conclusion: Typical antipsychotics and atypical antipsychotics affect different genes and biological function in the liver. Typical antipsychotic phenothiazines exert robust effects on gene expression in the liver that may lead to liver toxicity. The genes found in the current study may benefit antipsychotic drug development with better therapeutic and side effect profiles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Cost-effectiveness analysis of schizophrenic patient care settings: impact of an atypical antipsychotic under long-acting injection formulation].Encephale. 2005 Mar-Apr;31(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82390-5. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 15959450 Review. French.
-
Atypical antipsychotics: mechanism of action.Can J Psychiatry. 2002 Feb;47(1):27-38. Can J Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 11873706 Review.
-
Weight gain and antipsychotic medication: differences between antipsychotic-free and treatment periods.J Clin Psychiatry. 2001 Sep;62(9):694-700. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v62n0906. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11681765
-
Effectiveness and cost of atypical versus typical antipsychotic treatment for schizophrenia in routine care.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2008 Jun;11(2):89-97. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2008. PMID: 18509216
-
Effect of switching antipsychotics on antiparkinsonian medication use in schizophrenia: population-based study.Br J Psychiatry. 2005 Aug;187:137-42. doi: 10.1192/bjp.187.2.137. Br J Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16055824
Cited by
-
Antipsychotic drug use complicates assessment of gene expression changes associated with schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Mar 17;13(1):93. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02392-8. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36932057 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in quetiapine treated first-episode psychosis.Schizophr Res Treatment. 2014;2014:719395. doi: 10.1155/2014/719395. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Schizophr Res Treatment. 2014. PMID: 24672724 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship between the Level of Anterior Cingulate Cortex Metabolites, Brain-Periphery Redox Imbalance, and the Clinical State of Patients with Schizophrenia and Personality Disorders.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 3;10(9):1272. doi: 10.3390/biom10091272. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32899276 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational protein modifications in schizophrenia.NPJ Schizophr. 2020 Mar 2;6(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41537-020-0093-9. NPJ Schizophr. 2020. PMID: 32123175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-induced liver injury associated with atypical generation antipsychotics from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS).BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 30;25(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00782-2. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39215339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bender S, Grohmann R, Engel RR, Degner D, Dittmann-Balcar A, Ruther E. Severe adverse drug reactions in psychiatric inpatients treated with neuroleptics. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2004;37:S46–53. - PubMed
-
- Ozcanli T, Erdogan A, Ozdemir S, Onen B, Ozmen M, Doksat K, Sonsuz A. Severe liver enzyme elevations after three years of olanzapine treatment: a case report and review of olanzapine associated hepatotoxicity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006;30:1163–1166. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.03.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

