Identification and functional characterization of microRNAs involved in the malignant progression of gliomas
- PMID: 19775293
- PMCID: PMC8094849
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00328.x
Identification and functional characterization of microRNAs involved in the malignant progression of gliomas
Abstract
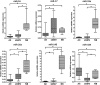
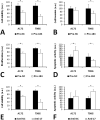
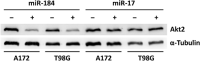
Diffuse astrocytoma of World Health Organization (WHO) grade II has an inherent tendency to spontaneously progress to anaplastic astrocytoma WHO grade III or secondary glioblastoma WHO grade IV. We explored the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in glioma progression by investigating the expression profiles of 157 miRNAs in four patients with primary WHO grade II gliomas that spontaneously progressed to WHO grade IV secondary glioblastomas. Thereby, we identified 12 miRNAs (miR-9, miR-15a, miR-16, miR-17, miR-19a, miR-20a, miR-21, miR-25, miR-28, miR-130b, miR-140 and miR-210) showing increased expression, and two miRNAs (miR-184 and miR-328) showing reduced expression upon progression. Validation experiments on independent series of primary low-grade and secondary high-grade astrocytomas confirmed miR-17 and miR-184 as promising candidates, which were selected for functional analyses. These studies revealed miRNA-specific influences on the viability, proliferation, apoptosis and invasive growth properties of A172 and T98G glioma cells in vitro. Using mRNA and protein expression profiling, we identified distinct sets of transcripts and proteins that were differentially expressed after inhibition of miR-17 or overexpression of miR-184 in glioma cells. Taken together, our results support an important role of altered miRNA expression in gliomas, and suggest miR-17 and miR-184 as interesting candidates contributing to glioma progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MiRNA expression profiling in human gliomas: upregulated miR-363 increases cell survival and proliferation.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):14035-14048. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5273-x. Epub 2016 Aug 6. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27495233
-
MiR-16-5p is frequently down-regulated in astrocytic gliomas and modulates glioma cell proliferation, apoptosis and response to cytotoxic therapy.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019 Aug;45(5):441-458. doi: 10.1111/nan.12532. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30548945
-
Up-regulation of microRNA-15b correlates with unfavorable prognosis and malignant progression of human glioma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4943-52. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191187 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as efficient biomarkers in high-grade gliomas.Folia Neuropathol. 2016;54(4):369-374. doi: 10.5114/fn.2016.64812. Folia Neuropathol. 2016. PMID: 28139816 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in adult high-grade gliomas: Mechanisms of chemotherapeutic resistance and their clinical relevance.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Mar;172:116277. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116277. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38377734 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxic glioma-derived exosomal miR-25-3p promotes macrophage M2 polarization by activating the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 16;22(1):628. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02888-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39407269 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic, epigenomic and transcriptomic landscape of glioblastoma.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Dec;39(8):1591-1611. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01414-8. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39180605 Review.
-
Circulating Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: Advances and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7974. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147974. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid Biopsy in Whole Blood for Identification of Gene Expression Patterns (mRNA and miRNA) Associated with Recurrence of Glioblastoma WHO CNS Grade 4.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;16(13):2345. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132345. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001407 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenols Modulate the miRNAs Expression that Involved in Glioblastoma.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(21):1953-1969. doi: 10.2174/0113895575304605240408105201. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38639278 Review.
References
-
- Balss J, Meyer J, Mueller W, Korshunov A, Hartmann C, Von Deimling A (2008) Analysis of the IDH1 codon 132 mutation in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol 116:597–602. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Leva GD, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE et al (2005) A microRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 353:1793–1801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

