3D Finite Element Meshing from Imaging Data
- PMID: 19777144
- PMCID: PMC2748876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cma.2004.11.026
3D Finite Element Meshing from Imaging Data
Abstract
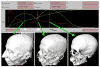
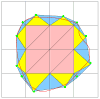
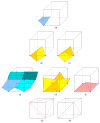
This paper describes an algorithm to extract adaptive and quality 3D meshes directly from volumetric imaging data. The extracted tetrahedral and hexahedral meshes are extensively used in the Finite Element Method (FEM). A top-down octree subdivision coupled with the dual contouring method is used to rapidly extract adaptive 3D finite element meshes with correct topology from volumetric imaging data. The edge contraction and smoothing methods are used to improve the mesh quality. The main contribution is extending the dual contouring method to crack-free interval volume 3D meshing with feature sensitive adaptation. Compared to other tetrahedral extraction methods from imaging data, our method generates adaptive and quality 3D meshes without introducing any hanging nodes. The algorithm has been successfully applied to constructing the geometric model of a biomolecule in finite element calculations.
Figures
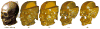
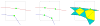
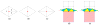
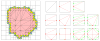
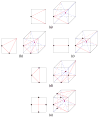
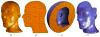
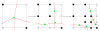

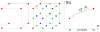





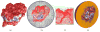
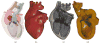


Similar articles
-
Quality Meshing of Implicit Solvation Models of Biomolecular Structures.Comput Aided Geom Des. 2006 Aug 1;23(6):510-530. doi: 10.1016/j.cagd.2006.01.008. Comput Aided Geom Des. 2006. PMID: 19809581 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive and Quality Quadrilateral/Hexahedral Meshing from Volumetric Data.Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2006 Feb 1;195(9):942-960. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2005.02.016. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2006. PMID: 19750180 Free PMC article.
-
Feature-Sensitive Tetrahedral Mesh Generation with Guaranteed Quality.Comput Aided Des. 2012 May 1;44(5):400-412. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2012.01.002. Comput Aided Des. 2012. PMID: 22328787 Free PMC article.
-
A voxel-based finite element model for the prediction of bladder deformation.Med Phys. 2012 Jan;39(1):55-65. doi: 10.1118/1.3668060. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22225275
-
A Robust Adaptive Mesh Generation Algorithm: A Solution for Simulating 2D Crack Growth Problems.Materials (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;16(19):6481. doi: 10.3390/ma16196481. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37834618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An atlas-based geometry pipeline for cardiac Hermite model construction and diffusion tensor reorientation.Med Image Anal. 2012 Aug;16(6):1130-41. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Med Image Anal. 2012. PMID: 22841777 Free PMC article.
-
Image-based modeling for better understanding and assessment of atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability: data, modeling, validation, uncertainty and predictions.J Biomech. 2014 Mar 3;47(4):834-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2014.01.012. Epub 2014 Jan 14. J Biomech. 2014. PMID: 24480706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PROTO-PLASM: parallel language for adaptive and scalable modelling of biosystems.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2008 Sep 13;366(1878):3045-65. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2008.0076. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2008. PMID: 18559320 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Meshing of Implicit Solvation Models of Biomolecular Structures.Comput Aided Geom Des. 2006 Aug 1;23(6):510-530. doi: 10.1016/j.cagd.2006.01.008. Comput Aided Geom Des. 2006. PMID: 19809581 Free PMC article.
-
New software developments for quality mesh generation and optimization from biomedical imaging data.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014;113(1):226-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014. PMID: 24252469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bajaj C, Coyle E, Lin KN. Arbitrary topology shape reconstruction from planar cross sections. Graphical Modeling and Image Processing. 1996;58(6):524–543.
-
- Bajaj C, Coyle E, Lin KN. Tetrahedral meshes from planar cross sections. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. 1999;179:31–52.
-
- Bajaj C, Pascucci V, Schikore D. Fast isocontouring for improved interactivity. Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Volume Visualization. 1996:39–46.
-
- Bajaj C, Pascucci V, Schikore D. The contour spectrum. IEEE Visualization. 1997:167–174.
-
- Bajaj C, Wu Q, Xu G. ICES Technical Report. Vol. 301. The Univ. of Texas at Austin; 2002. Level set based volume anisotropic diffusion.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
