Variant near ADAMTS9 known to associate with type 2 diabetes is related to insulin resistance in offspring of type 2 diabetes patients--EUGENE2 study
- PMID: 19789630
- PMCID: PMC2747270
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007236
Variant near ADAMTS9 known to associate with type 2 diabetes is related to insulin resistance in offspring of type 2 diabetes patients--EUGENE2 study
Abstract
Background: A meta-analysis combining results from three genome-wide association studies and followed by large-scale replication identified six novel type 2 diabetes loci. Subsequent studies of the effect of these variants on estimates of the beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity have been inconclusive. We examined these variants located in or near the JAZF1 (rs864745), THADA (rs7578597), TSPAN8 (rs7961581), ADAMTS9 (rs4607103), NOTCH2 (rs10923931) and the CDC123/CAMK1D (rs12779790) genes for associations with measures of pancreatic beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity.
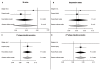
Methodology/results: Oral and intravenous glucose stimulated insulin release (n = 849) and insulin sensitivity (n = 596) estimated from a hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp were measured in non-diabetic offspring of type 2 diabetic patients from five European populations. Assuming an additive genetic model the diabetes-associated major C-allele of rs4607103 near ADAMTS9 associated with reduced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (p = 0.002) during a hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp. However, following intravenous and oral administration of glucose serum insulin release was increased in individuals with the C-allele (p = 0.003 and p = 0.01, respectively). A meta-analyse combining clamp and IVGTT data from a total of 905 non-diabetic individuals showed that the C-risk allele associated with decreased insulin sensitivity (p = 0.003) and increased insulin release (p = 0.002). The major T-allele of the intronic JAZF1 rs864745 conferring increased diabetes risk was associated with increased 2(nd) phase serum insulin release during an IVGTT (p = 0.03), and an increased fasting serum insulin level (p = 0.001). The remaining variants did not show any associations with insulin response, insulin sensitivity or any other measured quantitative traits.
Conclusion: The present studies suggest that the diabetogenic impact of the C-allele of rs4607103 near ADAMTS9 may in part be mediated through decreased insulin sensitivity of peripheral tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association testing of novel type 2 diabetes risk alleles in the JAZF1, CDC123/CAMK1D, TSPAN8, THADA, ADAMTS9, and NOTCH2 loci with insulin release, insulin sensitivity, and obesity in a population-based sample of 4,516 glucose-tolerant middle-aged Danes.Diabetes. 2008 Sep;57(9):2534-40. doi: 10.2337/db08-0436. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18567820 Free PMC article.
-
Novel meta-analysis-derived type 2 diabetes risk loci do not determine prediabetic phenotypes.PLoS One. 2008 Aug 20;3(8):e3019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003019. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18714373 Free PMC article.
-
Gene variants in the novel type 2 diabetes loci CDC123/CAMK1D, THADA, ADAMTS9, BCL11A, and MTNR1B affect different aspects of pancreatic beta-cell function.Diabetes. 2010 Jan;59(1):293-301. doi: 10.2337/db09-1048. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 19833888 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of type 2 diabetes susceptibility variants on quantitative glycemic traits reveals mechanistic heterogeneity.Diabetes. 2014 Jun;63(6):2158-71. doi: 10.2337/db13-0949. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24296717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiologic characterization of type 2 diabetes-related loci.Curr Diab Rep. 2010 Dec;10(6):485-97. doi: 10.1007/s11892-010-0154-y. Curr Diab Rep. 2010. PMID: 20886378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental and extracellular matrix-remodeling processes in rosiglitazone-exposed neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.Pharmacogenomics. 2014 Apr;15(6):759-74. doi: 10.2217/pgs.14.39. Pharmacogenomics. 2014. PMID: 24897284 Free PMC article.
-
ADAMTS proteins in human disorders.Matrix Biol. 2018 Oct;71-72:225-239. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29885460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ADAMTS9 gene is associated with cognitive aging in the elderly in a Taiwanese population.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 22;12(2):e0172440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172440. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28225792 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic predictors of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes in a predisposed population--A prospective cohort study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2015 Sep 25;15:51. doi: 10.1186/s12902-015-0048-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2015. PMID: 26407933 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of type 2 diabetes in European populations.J Diabetes. 2012 Sep;4(3):203-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2012.00224.x. J Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22781158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, Dina C, Shen L. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007;445:881–885. - PubMed
-
- Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Jansdottir T. A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2007;39:770–775. - PubMed
-
- Saxena R, Voight BF, Lyssenko V, Burtt NP, de Bakker PIN. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Loci for Type 2 Diabetes and Triglyceride Levels. Science. 2007;316:1331–1336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

