ConservedPrimers 2.0: a high-throughput pipeline for comparative genome referenced intron-flanking PCR primer design and its application in wheat SNP discovery
- PMID: 19825183
- PMCID: PMC2765976
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-331
ConservedPrimers 2.0: a high-throughput pipeline for comparative genome referenced intron-flanking PCR primer design and its application in wheat SNP discovery
Abstract
Background: In some genomic applications it is necessary to design large numbers of PCR primers in exons flanking one or several introns on the basis of orthologous gene sequences in related species. The primer pairs designed by this _target gene approach are called "intron-flanking primers" or because they are located in exonic sequences which are usually conserved between related species, "conserved primers". They are useful for large-scale single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery and marker development, especially in species, such as wheat, for which a large number of ESTs are available but for which genome sequences and intron/exon boundaries are not available. To date, no suitable high-throughput tool is available for this purpose.
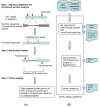
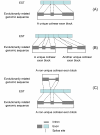
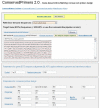
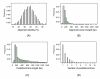
Results: We have developed, the ConservedPrimers 2.0 pipeline, for designing intron-flanking primers for large-scale SNP discovery and marker development, and demonstrated its utility in wheat. This tool uses non-redundant wheat EST sequences, such as wheat contigs and singleton ESTs, and related genomic sequences, such as those of rice, as inputs. It aligns the ESTs to the genomic sequences to identify unique colinear exon blocks and predicts intron lengths. Intron-flanking primers are then designed based on the intron/exon information using the Primer3 core program or BatchPrimer3. Finally, a tab-delimited file containing intron-flanking primer pair sequences and their primer properties is generated for primer ordering and their PCR applications. Using this tool, 1,922 bin-mapped wheat ESTs (31.8% of the 6,045 in total) were found to have unique colinear exon blocks suitable for primer design and 1,821 primer pairs were designed from these single- or low-copy genes for PCR amplification and SNP discovery. With these primers and subsequently designed genome-specific primers, a total of 1,527 loci were found to contain one or more genome-specific SNPs.
Conclusion: The ConservedPrimers 2.0 pipeline for designing intron-flanking primers was developed and its utility demonstrated. The tool can be used for SNP discovery, genetic variation assays and marker development for any _target genome that has abundant ESTs and a related reference genome that has been fully sequenced. The ConservedPrimers 2.0 pipeline has been implemented as a command-line tool as well as a web application. Both versions are freely available at http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/demos/ConservedPrimers/.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BatchPrimer3: a high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 May 29;9:253. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-253. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18510760 Free PMC article.
-
PCR-based landmark unique gene (PLUG) markers effectively assign homoeologous wheat genes to A, B and D genomes.BMC Genomics. 2007 May 30;8:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-135. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17535443 Free PMC article.
-
SSCP-SNP in pearl millet--a new marker system for comparative genetics.Theor Appl Genet. 2005 May;110(8):1467-72. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-1981-0. Epub 2005 Apr 5. Theor Appl Genet. 2005. PMID: 15809850
-
Progress on methods for acquiring flanking genomic sequence.Yi Chuan. 2022 Apr 20;44(4):313-321. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.21-415. Yi Chuan. 2022. PMID: 35437239 Review.
-
Designing Allele-Specific Competitive-Extension PCR-Based Assays for High-Throughput Genotyping and Gene Characterization.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 1;9:773956. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.773956. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35300118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fine mapping of wheat stripe rust resistance gene Yr26 based on collinearity of wheat with Brachypodium distachyon and rice.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057885. Epub 2013 Mar 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23526955 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic divergence during speciation driven by adaptation to altitude.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Dec;30(12):2553-67. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst168. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 24077768 Free PMC article.
-
Solar Radiation-Associated Adaptive SNP Genetic Differentiation in Wild Emmer Wheat, Triticum dicoccoides.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Mar 14;8:258. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00258. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28352272 Free PMC article.
-
Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Aug;40(15):e115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks596. Epub 2012 Jun 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22730293 Free PMC article.
-
Fine physical and genetic mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene MlIW172 originating from wild emmer (Triticum dicoccoides).PLoS One. 2014 Jun 23;9(6):e100160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100160. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24955773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rostoks N, Mudie S, Cardle L, Russell J, Ramsay L, Booth A, Svensson JT, Wanamaker SI, Walia H, Rodriguez EM, et al. Genome-wide SNP discovery and linkage analysis in barley based on genes responsive to abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005;274:515–527. doi: 10.1007/s00438-005-0046-z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

