Reciprocal regulation of c-Src and STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 19861436
- PMCID: PMC2935176
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0767
Reciprocal regulation of c-Src and STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) is downstream of growth factor and cytokine receptors, and regulates key oncogenic pathways in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Activation of STAT3 by cellular Src (c-Src) promotes tumor progression. We hypothesized that c-Src inhibition could activate STAT3 by inducing a homeostatic feedback loop, contributing to c-Src inhibitor resistance.
Experimental design: The effects of c-Src inhibition on total and phosphorylated STAT3 were measured in NSCLC cell lines and in murine xenograft models by Western blotting. c-Src and STAT3 activity as indicated by phosphorylation was determined in 46 human tumors and paired normal lung by reverse phase protein array. Modulation of dasatinib (c-Src inhibitor) cytotoxicity by STAT3 knockdown was measured by MTT, cell cycle, and apoptosis assays.
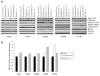
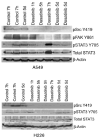
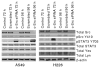
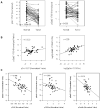
Results: Depletion of c-Src by small interfering RNA or sustained inhibition by dasatinib increased pSTAT3, which could be blocked by inhibition of JAK. Similarly, in vivo pSTAT3 levels initially decreased but were strongly induced after sustained dasatinib treatment. In human tumors, phosphorylation of the autoinhibitory site of c-Src (Y527) correlated with STAT3 phosphorylation (r = 0.64; P = 2.5 x 10(-6)). STAT3 knockdown enhanced the cytotoxicity of dasatinib.
Conclusions: c-Src inhibition leads to JAK-dependent STAT3 activation in vitro and in vivo. STAT3 knockdown enhances the cytotoxicity of dasatinib, suggesting a compensatory pathway that allows NSCLC survival. Data from human tumors showed a reciprocal regulation of c-Src and STAT3 activation, suggesting that this compensatory pathway functions in human NSCLC. These results provide a rationale for combining c-Src and STAT3 inhibition to improve clinical responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multicellular Effects of STAT3 in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 11;13(24):6228. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246228. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abrogation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 reactivation after Src kinase inhibition results in synergistic antitumor effects.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Jul 15;13(14):4233-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2981. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17634553
-
Sustained Src inhibition results in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation and cancer cell survival via altered Janus-activated kinase-STAT3 binding.Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 1;69(5):1958-65. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2944. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19223541 Free PMC article.
-
Activated epidermal growth factor receptor-Stat-3 signaling promotes tumor survival in vivo in non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 1;11(23):8288-94. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0827. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16322287
-
Effects of Src kinase inhibition induced by dasatinib in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines treated with cisplatin.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Nov;8(11):3066-74. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0151. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19861409
Cited by
-
A YAP/FOXM1 axis mediates EMT-associated EGFR inhibitor resistance and increased expression of spindle assembly checkpoint components.Sci Transl Med. 2020 Sep 2;12(559):eaaz4589. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz4589. Sci Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32878980 Free PMC article.
-
A network-based biomarker approach for molecular investigation and diagnosis of lung cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2011 Jan 6;4:2. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21211025 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5A-mediated SOCS2 expression regulates Jak2 and STAT3 activity following c-Src inhibition in head and neck squamous carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;18(1):127-39. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1889. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22090359 Free PMC article.
-
The role of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway on apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma cell line PC-9 induced by icotinib.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Apr 15;8(4):1730-7. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27186296 Free PMC article.
-
Multicellular Effects of STAT3 in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 11;13(24):6228. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246228. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2008. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008.
-
- Minna J, Schiller J. In: Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 17. Kasper DFA, Longo DL, editors. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2008.
-
- Johnson FM, Gallick GE. SRC family nonreceptor tyrosine kinases as molecular _targets for cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007;7:651–9. - PubMed
-
- Thomas SM, Brugge JS. Cellular functions regulated by Src family kinases. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:513–609. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

