Accuracy of monofilament testing to diagnose peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review
- PMID: 19901316
- PMCID: PMC2775618
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.1016
Accuracy of monofilament testing to diagnose peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: We wanted to summarize evidence about the diagnostic accuracy of the 5.07/10-g monofilament test in peripheral neuropathy.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of studies in which the accuracy of the 5.07/10-g monofilament was evaluated to detect peripheral neuropathy of any cause using nerve conduction as reference standard. Methodological quality was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) tool.
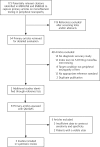
Results: We reviewed 173 titles and abstracts of articles to identify 54 potentially eligible studies, of which 3 were finally selected for data synthesis. All studies were limited to patients with diabetes mellitus and showed limitations according to the QUADAS tool. Sensitivity ranged from 41% to 93% and specificity ranged from 68% to 100%. Because of the heterogenous nature of the studies, a meta-analysis could not be accomplished.
Conclusions: Despite the frequent use of monofilament testing, little can be said about the test accuracy for detecting neuropathy in feet without visible ulcers. Optimal test application and defining a threshold should have priority in evaluating monofilament testing, as this test is advocated in many clinical guidelines. Accordingly, we do not recommend the sole use of monofilament testing to diagnose peripheral neuropathy.
Figures
Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: Accuracy of monofilament testing for diagnosing peripheral neuropathy of the feet varies.Ann Intern Med. 2010 May 18;152(10):JC5-11. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-02011. Ann Intern Med. 2010. PMID: 20479016 No abstract available.
-
[Monofilament test diagnose peripheral neuropathy].Praxis (Bern 1994). 2010 Jun 23;99(13):803-4. doi: 10.1024/1661-8157/a000174. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2010. PMID: 20572003 German. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Monofilament Tests for Detecting Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:8787261. doi: 10.1155/2017/8787261. Epub 2017 Oct 8. J Diabetes Res. 2017. PMID: 29119118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical evaluation of a new device in the assessment of peripheral sensory neuropathy in diabetes.Diabet Med. 2012 Dec;29(12):1553-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2012.03729.x. Diabet Med. 2012. PMID: 22672257
-
[Examination of peripheral sensibility. Vibration test is more sensitive than monofilament test].Lakartidningen. 2002 Mar 21;99(12):1339-40. Lakartidningen. 2002. PMID: 11998167 Swedish.
-
[Evaluation of the four simple methods in the diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Oct 17;86(38):2707-10. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17199983 Chinese.
-
Screening for peripheral neuropathies in children with diabetes: a systematic review.Pediatrics. 2014 May;133(5):e1324-30. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-3645. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Pediatrics. 2014. PMID: 24709928 Review.
Cited by
-
Plantar pressure distribution and altered postural control in multibacillary leprosy patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 24;24(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08749-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38267905 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the 5.07 monofilament test for diabetes polyneuropathy: influence of age, sex, neuropathic pain and neuropathy severity.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2023 Nov;11(6):e003545. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2023-003545. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2023. PMID: 37989346 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Sciatic Nerve Injury Repairs: A Systematic Review.Eplasty. 2023 Jul 14;23:e42. eCollection 2023. Eplasty. 2023. PMID: 37664809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of Diabetes Mellitus Progression Using Supervised Machine Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 May 11;23(10):4658. doi: 10.3390/s23104658. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37430572 Free PMC article.
-
Plantar threshold sensitivity assessment using an automated tool-Clinical assessment comparison between a control population without type 2 diabetes mellitus, and populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with and without neuropathy symptoms.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 7;18(7):e0286559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286559. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37418442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl 1):S12–S54. - PubMed
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, et al.; American Diabetes Association. Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(4):956–962. - PubMed
-
- Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, et al. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology. 1993;43(4):817–824. - PubMed
-
- England JD, Gronseth GS, Franklin G, et al. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy: a definition for clinical research: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2005;64(2):199–207. - PubMed
-
- Dutch Association of Neurology (NVN), Dutch Association of Clinical Neurophysiology (NVKNF). Guideline Polyneuropathy of the Dutch Institute for Healthcare Improvement (CBO). Alphen a/d Rijn, the Netherlands: van Zuiden; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical