Necroptosis as an alternative form of programmed cell death
- PMID: 20045303
- PMCID: PMC2854308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.12.003
Necroptosis as an alternative form of programmed cell death
Abstract
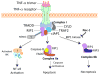
The family of death receptors plays a critical role in regulating cell number and eliminating harmful or virally infected cells. Agonistic stimulation of death receptors is known to lead two alternative cell fates by either activating NF-kappaB to promote cell survival or inducing apoptosis to lead to cell death; and now a third pathway, termed necroptosis or programmed necrosis has been identified. Interestingly, a death-domain containing kinase, RIP1, is involved in mediating all three pathways, with its kinase activity specifically involved in regulating necroptosis. The availability of necrostatin-1, a specific inhibitor of RIP1 kinase, made it possible to dissect the distinct functional domains of RIP1. Recent genome-wide siRNA screens have identified multiple players of necroptosis that may interact with and/or regulate RIP1 kinase and mediate the signaling pathway and execution of necroptosis. Necroptosis and necrostatins provide an exciting new opportunity for developing new treatments for multiple human diseases involving necrosis and inflammation.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RIP1, RIP3, and MLKL Contribute to Cell Death Caused by Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin.mBio. 2019 Dec 17;10(6):e02985-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02985-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31848291 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Microglial Parkin Inhibits Necroptosis and Contributes to Neuroinflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;56(4):2990-3004. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1264-9. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30074231
-
Control of life-or-death decisions by RIP1 kinase.Annu Rev Physiol. 2014;76:129-50. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170259. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24079414 Review.
-
Connections between various trigger factors and the RIP1/ RIP3 signaling pathway involved in necroptosis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(12):7069-74. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.12.7069. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24460252 Review.
-
Detection of Necroptosis in Ligand-Mediated and Hypoxia-Induced Injury of Hepatocytes Using a Novel Optic Probe-Detecting Receptor-Interacting Protein (RIP)1/RIP3 Binding.Oncol Res. 2018 Apr 10;26(3):503-513. doi: 10.3727/096504017X15005102445191. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 28770700 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Maduramicin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in myoblast cells.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 22;9(12):e115652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115652. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25531367 Free PMC article.
-
Ciprofloxacin modulates cytokine/chemokine profile in serum, improves bone marrow repopulation, and limits apoptosis and autophagy in ileum after whole body ionizing irradiation combined with skin-wound trauma.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058389. Epub 2013 Mar 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23520506 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring the clearance of apoptotic and necrotic cells in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1004:183-202. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-383-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23733578 Free PMC article.
-
Stress- and Rho-activated ZO-1-associated nucleic acid binding protein binding to p21 mRNA mediates stabilization, translation, and cell survival.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 3;109(27):10897-902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118822109. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22711822 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-interacting protein in malignant digestive neoplasms.J Cancer. 2021 May 19;12(14):4362-4371. doi: 10.7150/jca.57076. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34093836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Degterev A, Yuan J. Expansion and evolution of cell death programmes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA, Yuan J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:112–119. Using a cell-based screen, the authors identified necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), a highly specific and potent inhibitor of necroptosis and demonstrated the role of necroptosis in mouse model of stroke. - PubMed
-
- Holler N, Zaru R, Micheau O, Thome M, Attinger A, Valitutti S, Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Seed B, Tschopp J. Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:489–495. The authors demonstrated the requirement of RIP1 kinase activity in mediating this alternative necrotic cell death activated by death receptors. - PubMed
-
- Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch’en IL, Korkina O, Teng X, Abbott D, Cuny GD, Yuan C, Wagner G, et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular _target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4:313–321. The authors demonstrated that necrostatins directly _target RIP1 kinase activity to inhibit necroptosis. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M, Chan FK. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell. 2009;137:1112–1123. The authors demonstrated the role of RIP3 in mediating necroptosis and the interaction of RIP1 and RIP3. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

