Regulating survival and development in the retina: key roles for simple sphingolipids
- PMID: 20100817
- PMCID: PMC3035489
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R003442
Regulating survival and development in the retina: key roles for simple sphingolipids
Abstract
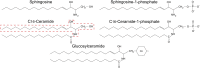
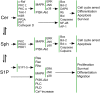
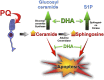
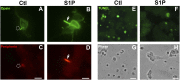
Many sphingolipids have key functions in the regulation of crucial cellular processes. Ceramide (Cer) and sphingosine (Sph) induce growth arrest and cell death in multiple situations of cellular stress. On the contrary, sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), the product of Sph phosphorylation, promotes proliferation, differentiation, and survival in different cell systems. This review summarizes the roles of these simple sphingolipids in different tissues and then analyzes their possible functions in the retina. Alterations in proliferation, neovascularization, differentiation, and cell death are critical in major retina diseases and collective evidence points to a role for sphingolipids in these processes. Cer induces inflammation and apoptosis in endothelial and retinal pigmented epithelium cells, leading to several retinopathies. S1P can prevent this death but also promotes cell proliferation that might lead to neovascularization and fibrosis. Recent data support Cer and Sph as crucial mediators in the induction of photoreceptor apoptosis in diverse models of oxidative damage and neurodegeneration, and suggest that regulating their metabolism can prevent this death. New evidence proposes a central role for S1P controlling photoreceptor survival and differentiation. Finally, this review discusses the ability of trophic factors to regulate sphingolipid metabolism and transactivate S1P signaling pathways to control survival and development in retina photoreceptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sphingolipids as Emerging Mediators in Retina Degeneration.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jun 11;13:246. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00246. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31244608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on sphingolipids: Spotlight on retinopathy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Nov;143:112197. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112197. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34560541 Review.
-
Sphingolipids as critical players in retinal physiology and pathology.J Lipid Res. 2021;62:100037. doi: 10.1194/jlr.TR120000972. Epub 2021 Feb 6. J Lipid Res. 2021. PMID: 32948663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism and biological functions of two phosphorylated sphingolipids, sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide 1-phosphate.Prog Lipid Res. 2007 Mar;46(2):126-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2007.03.001. Epub 2007 Mar 14. Prog Lipid Res. 2007. PMID: 17449104 Review.
-
Role of bioactive sphingolipids in physiology and pathology.Essays Biochem. 2020 Sep 23;64(3):579-589. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190091. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32579188 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential roles of neutral ceramidase and sphingosine in mitochondrial dysfunction due to traumatic brain injury.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 9;289(19):13142-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.530311. Epub 2014 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24659784 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors are essential mediators of eyelid closure during embryonic development.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29882-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.510099. Epub 2013 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24003216 Free PMC article.
-
Whole exome sequencing of extreme age-related macular degeneration phenotypes.Mol Vis. 2016 Aug 29;22:1062-76. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 27625572 Free PMC article.
-
A prokaryotic S1P lyase degrades extracellular S1P in vitro and in vivo: implication for treating hyperproliferative disorders.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022436. Epub 2011 Aug 1. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829623 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide signaling in retinal degeneration.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;723:553-8. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0631-0_70. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22183377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nishizuka Y. 1992. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 258: 607–614. - PubMed
-
- Piomelli D. 1993. Arachidonic acid in cell signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 5: 274–280. - PubMed
-
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., Stafforini D. M., McIntyre T. M. 2000. Platelet-activating factor and related lipid mediators. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69: 419–445. - PubMed
-
- Irvine R. F. 1992. Inositol lipids in cell signalling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 4: 212–219. - PubMed
-
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M. 1986. Protein kinase C activation in mixed micelles. Mechanistic implications of phospholipid, diacylglycerol, and calcium interdependencies. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 7184–7190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

