MicroRNA-27b contributes to lipopolysaccharide-mediated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) mRNA destabilization
- PMID: 20164187
- PMCID: PMC2852921
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.066399
MicroRNA-27b contributes to lipopolysaccharide-mediated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) mRNA destabilization
Abstract
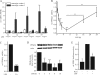
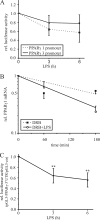
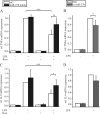
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) gained considerable interest as a therapeutic _target during chronic inflammatory diseases. Remarkably, the pathogenesis of diseases such as multiple sclerosis or Alzheimer is associated with impaired PPARgamma expression. Considering that regulation of PPARgamma expression during inflammation is largely unknown, we were interested in elucidating underlying mechanisms. To this end, we initiated an inflammatory response by exposing primary human macrophages to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and observed a rapid decline of PPARgamma1 expression. Because promoter activities were not affected by LPS, we focused on mRNA stability and noticed a decreased mRNA half-life. As RNA stability is often regulated via 3'-untranslated regions (UTRs), we analyzed the impact of the PPARgamma-3'-UTR by reporter assays using specific constructs. LPS significantly reduced luciferase activity of the pGL3-PPARgamma-3'-UTR, suggesting that PPARgamma1 mRNA is destabilized. Deletion or mutation of a potential microRNA-27a/b (miR-27a/b) binding site within the 3'-UTR restored luciferase activity. Moreover, inhibition of miR-27b, which was induced upon LPS exposure, partially reversed PPARgamma1 mRNA decay, whereas miR-27b overexpression decreased PPARgamma1 mRNA content. In addition, LPS further reduced this decay. The functional relevance of miR-27b-dependent PPARgamma1 decrease was proven by inhibition or overexpression of miR-27b, which affected LPS-induced expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) and interleukin (IL)-6. We provide evidence that LPS-induced miR-27b contributes to destabilization of PPARgamma1 mRNA. Understanding molecular mechanisms decreasing PPARgamma might help to better appreciate inflammatory diseases.
Figures

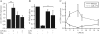
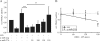
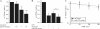
Similar articles
-
PPARγ inhibits HMGB1 expression through upregulation of miR-142-3p in vitro and in vivo.Cell Signal. 2016 Mar;28(3):158-164. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.12.013. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 26721185
-
Activation of PPARγ inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines production by upregulation of miR-124 in vitro and in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 May 6;486(3):726-731. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.03.106. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28342874
-
Sumoylation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma by apoptotic cells prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced NCoR removal from kappaB binding sites mediating transrepression of proinflammatory cytokines.J Immunol. 2008 Oct 15;181(8):5646-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.8.5646. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18832723 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ and microRNA 98 in Hypoxia-Induced Endothelin-1 Signaling.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Jan;54(1):136-46. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0337OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26098770 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates LPS-stimulated inflammatory response by regulating the PPARγ/NF-κB pathways in primary bovine mammary epithelial cells.Res Vet Sci. 2017 Jun;112:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Res Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28095338 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear Receptors and Lipid Sensing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1390:83-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-11836-4_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36107314
-
Comparative analysis of hepatic miRNA levels in male marathon mice reveals a link between obesity and endurance exercise capacities.J Comp Physiol B. 2016 Dec;186(8):1067-1078. doi: 10.1007/s00360-016-1006-0. Epub 2016 Jun 9. J Comp Physiol B. 2016. PMID: 27278158
-
Non-coding RNAs in immunoregulation and autoimmunity: Technological advances and critical limitations.J Autoimmun. 2023 Jan;134:102982. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102982. Epub 2022 Dec 31. J Autoimmun. 2023. PMID: 36592512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine receptor CCR6 expression is regulated by miR-518a-5p in colorectal cancer cells.J Transl Med. 2014 Feb 21;12:48. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-48. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24559209 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of betulinic acid on LPS-mediated inhibition of ABCA1 and cholesterol efflux through inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway and miR-33 expression.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 25;8(9):e74782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074782. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoecklin G., Anderson P. (2006) Adv. Immunol. 89, 1–37 - PubMed
-
- Winter J., Jung S., Keller S., Gregory R. I., Diederichs S. (2009) Nat. Cell Biol. 11, 228–234 - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A., Huntzinger E., Izaurralde E. (2008) Cell 132, 9–14 - PubMed
-
- Sheedy F. J., O'Neill L. A. (2008) Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, iii50–55 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

