VHL and PTEN loss coordinate to promote mouse liver vascular lesions
- PMID: 20221685
- PMCID: PMC2872996
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-010-9164-2
VHL and PTEN loss coordinate to promote mouse liver vascular lesions
Abstract
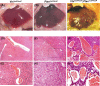
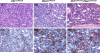
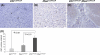
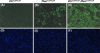
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) inactivation develops a tumor syndrome characterized by highly vascularized tumors as a result of hypoxia inducible factors (HIF) stabilization. The most common manifestation is the development of hemangioblastomas typically located in the central nervous system and other organs including the liver. PTEN (Phosphatase and tension homologue deleted on chromosome 10) inactivation also upregulates HIF-1alpha and may take part in promoting vascular lesions in tumors. The coordinate effect of loss of these tumor suppressors on HIF levels, and the subsequent effect on vascular lesion formation would elucidate the potential for mechanisms to modify HIF dosage supplementally and impact tumor phenotype. We therefore employed models of somatic conditional inactivation of Vhl, Pten, or both tumor suppressor genes in individual cells of the liver by Cre-loxP recombination to study the cooperativity of these two tumor suppressors in preventing tumor formation. Nine months after tumor suppressor inactivation, Vhl conditional deletion (Vhl (loxP/loxP)) mice showed no abnormalities, Pten conditional deletion (Pten (loxP/loxP)) mice developed liver steatosis and focal nodular expansion of hepatocytes containing lipid droplet and fat. Vhl and Pten conditional deletion (Vhl (loxP/loxP);Pten (loxP/loxP)) mice, however, developed multiple cavernous liver lesions reminiscent of hemangioblastoma. Liver hemangioblastomas in VHL disease may, therefore, require secondary mutation in addition to VHL loss of heterozygosity which is permissive for vascular lesion development or augments levels of HIF-1alpha.
Figures




Similar articles
-
EAF2 loss enhances angiogenic effects of Von Hippel-Lindau heterozygosity on the murine liver and prostate.Angiogenesis. 2011 Sep;14(3):331-43. doi: 10.1007/s10456-011-9217-1. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Angiogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21638067 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of the arylhydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt) suppresses von Hippel-Lindau disease-associated vascular tumors in mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;25(8):3163-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.8.3163-3172.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15798202 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha under normoxic conditions in renal carcinoma cells by von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene loss of function.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 16;19(48):5435-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203938. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11114720
-
The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene.Exp Cell Res. 2001 Mar 10;264(1):117-25. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.5139. Exp Cell Res. 2001. PMID: 11237528 Review.
-
The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene and kidney cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Sep 15;10(18 Pt 2):6290S-5S. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-sup-040025. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15448019 Review.
Cited by
-
EAF2 loss enhances angiogenic effects of Von Hippel-Lindau heterozygosity on the murine liver and prostate.Angiogenesis. 2011 Sep;14(3):331-43. doi: 10.1007/s10456-011-9217-1. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Angiogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21638067 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressive activity of prolyl isomerase Pin1 in renal cell carcinoma.Mol Oncol. 2011 Oct;5(5):465-74. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Mol Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21764651 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a reactive stroma associated with prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in EAF2 deficient mice.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 18;8(11):e79542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079542. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260246 Free PMC article.
-
Von Hippel-Lindau status influences phenotype of liver cancers arising from PTEN loss.Gastrointest Cancer. 2015 Feb 1;5:61-71. doi: 10.2147/GICTT.S72274. Gastrointest Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25844041 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling hypoxia signaling from oxygen sensing in the liver results in hypoketotic hypoglycemic death.Oncogene. 2011 May 5;30(18):2147-60. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.587. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21217781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGrath FP, et al. Case report: multiple hepatic and pulmonary haemangioblastomas—a new manifestation of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Clin Radiol. 1992;45(1):37–39. - PubMed
-
- Maher ER, Kaelin WG., Jr von Hippel-Lindau disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1997;76(6):381–391. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, et al. Suppression of growth of renal carcinoma cells by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Res. 1995;55(21):4804–4807. - PubMed
-
- Gnarra JR, et al. Mutations of the VHL tumour suppressor gene in renal carcinoma. Nat Genet. 1994;7(1):85–90. - PubMed
-
- Shuin T, et al. Frequent somatic mutations and loss of heterozygosity of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in primary human renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1994;54(11):2852–2855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

